Palo Alto Firewall
This section has instructions for collecting Palo Alto Firewall log messages and sending them to Sumo Logic to be ingested by CSE.
Sumo Logic CSE supports the default comma separated value (CSV), as well as Common Event Format (CEF) logs from Palo Alto Firewalls running PAN OS 10.0. This guide provides steps for collecting CSV format logs.
Step 1: Configure collection
In this step, you configure a Syslog Source to collect Palo Alto Firewall log messages. You can configure the source on an existing Installed Collector or create a new collector. If you’re going to use an existing collector, jump to Configure a Syslog Source below. Otherwise, create a new collector as described in Configure an Installed Collector below, and then create the Syslog Source on the collector.
Configure an Installed Collector
- In the Sumo Logic platform, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- Click Add Collector.
- Click Installed Collector.
- The Add Installed Collector popup appears.
- Download the appropriate collector for your operating system.
- Install the collector. Instructions for your preferred operating system and method of installation are available on the Installed Collectors page.
- Once the collector is installed, confirm it is available on the Collection page and select Edit.
- The Edit Collector popup appears.
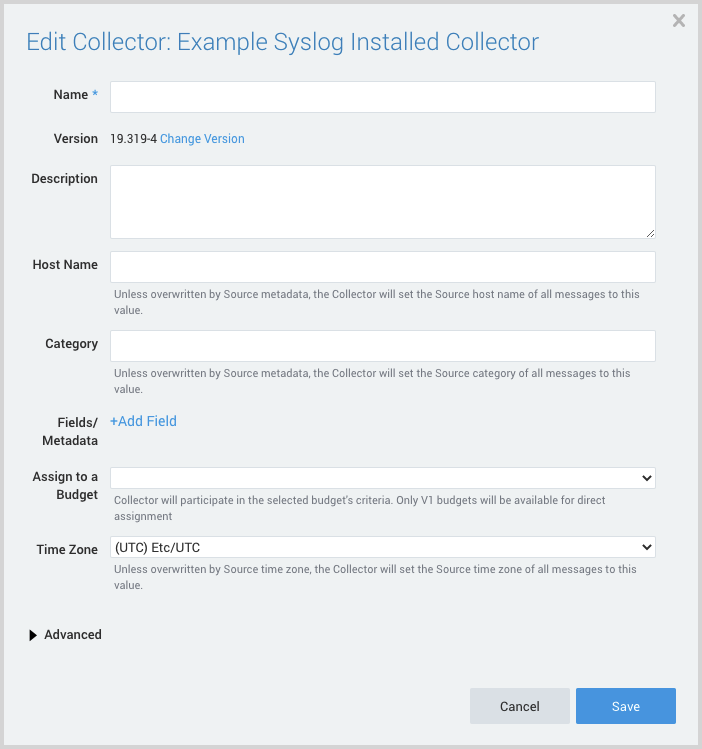
- Name. Provide a Name for the Collector.
- Description. (Optional)
- Category. Enter a string to tag the output collected from the source. The string that you supply will be saved in a metadata field called
_sourceCategory. - Fields.
- If you are planning that all the sources you add to this collector will forward log messages to CSE, click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
_siemForwardand value is true. This will cause the collector to forward all of the logs collected by all of the sources on the collector to CSE. - If you are planning that all sources you add to this collector will use the same log parser (if they are the same type of log), click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
_parserwith the value /Parsers/System/Palo Alto/PAN Firewall CSV. This will cause all sources on the collector to use the specified parser. It’s also possible to configure individual sources to forward to CSE, as described in the following section
- If you are planning that all the sources you add to this collector will forward log messages to CSE, click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
- Click Save.
Configure a Syslog Source
- In Sumo Logic, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
- Navigate to the Installed Collector where you want to create the source.
- On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to an Installed Collector.
- Select Syslog.
- The page refreshes.
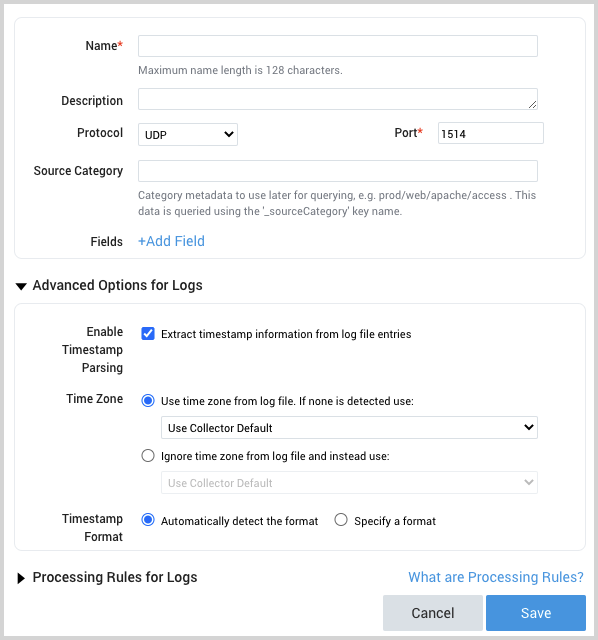
- Name. Enter a name for the source.
- Description. (Optional)
- Protocol. Select the protocol that your syslog-enabled devices are currently using to send syslog data, UDP or TCP. For more information, see Choosing TCP or UDP on the Syslog Source page.
- Port. Enter the port number for the Source to listen to. If the collector runs as root (default), use 514. Otherwise, consider 1514 or 5140. Make sure the devices are sending to the same port.
- Source Category. Enter a string to tag the output collected from the source. The string that you supply will be saved in a metadata field called
_sourceCategory. Make a note of the source category. You’ll supply it in Step 2 below. - Fields.
- If you have not configured the Installed Collector to forward all sources in the collector to CSE, click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
_siemForwardand value is true. - If you have not configured the Installed Collector to parse all sources in the collector with the same parser, click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
_parserwith the value /Parsers/System/Palo Alto/PAN Firewall CSV.
- If you have not configured the Installed Collector to forward all sources in the collector to CSE, click the +Add Field link, and add a field whose name is
- Click Save.
Step 2: Define destination for the logs
In this step you create a server profile where you can define the log destination. This will be the host name, port and protocol (TLS) of the Sumo Logic Cloud Syslog source.
To create a server profile specifying the log destination, do the following:
- Login to the Palo Alto Networks Web interface as an administrative user.
- Select Device tab > Server Profiles > Syslog.
- Click Add at the bottom of the screen and provide endpoint details and a profile name, such as
Sumo_Logs_Profile01. - In the Syslog Server Profile window, select the Servers tab and click Add.
- In the Servers window, specify the following information:
- Name:
Sumo_CloudSyslog_EndPoint01 - Syslog Server: Internal IP of Collector
- Transport: UDP
- Port: Port from Collector Setup
- Format: BSD
- Facility:
LOG_USER
- Name:
- In the Syslog Server Profile window, select the Custom Log Format tab, and use the following custom formats for the following log types:
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$host,$vsys,$cmd,$admin,$client,$result,$path,$before-change-detail,$after-change-detail,$seqno,$actionflags,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$vsys,$eventid,$object,,,$module,$severity,$opaque,$seqno,$actionflags,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name,$high_res_timestamp
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$src,$dst,$natsrc,$natdst,$rule,$srcuser,$dstuser,$app,$vsys,$from,$to,$inbound_if,$outbound_if,$logset,,$sessionid,$repeatcnt,$sport,$dport,$natsport,$natdport,$flags,$proto,$action,$bytes,$bytes_sent,$bytes_received,$packets,$start,\$elapsed,$category,,$seqno,$actionflags,$srcloc,$dstloc,,$pkts_sent,$pkts_received,$session_end_reason,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name,$action_source,$src_uuid,$dst_uuid,$tunnelid/$imsi,$monitortag/$imei,$parent_session_id,$parent_start_time,$tunnel,$assoc_id,$chunks,$chunks_sent,$chunks_received,$rule_uuid,$http2_connection,$link_change_count,$policy_id,\$link_switches,$sdwan_cluster,$sdwan_device_type,$sdwan_cluster_type,$sdwan_site,$dynusergroup_name,$xff_ip,$src_category,$src_profile,$src_model,$src_vendor,$src_osfamily,$src_osversion,$src_host,$src_mac,$dst_category,$dst_profile,$dst_model,$dst_vendor,$dst_osfamily,$dst_osversion,$dst_host,$dst_mac,$container_id,$pod_namespace,$pod_name,$src_edl,$dst_edl,$hostid,$serialnumber,$src_dag,$dst_dag,$session_owner,\$high_res_timestamp,$nsdsai_sst,$nsdsai_sd
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$src,$dst,$natsrc,$natdst,$rule,$srcuser,$dstuser,$app,$vsys,$from,$to,$inbound_if,$outbound_if,$logset,,$sessionid,$repeatcnt,$sport,$dport,$natsport,$natdport,$flags,$proto,$action,$misc,$threatid,$category,$severity,$direction,\$seqno,$actionflags,$srcloc,$dstloc,,$contenttype,$pcap_id,$filedigest,$cloud,$url_idx,$user_agent,$filetype,$xff,$referer,$sender,$subject,$recipient,$reportid,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,\$vsys_name,$device_name,,$src_uuid,$dst_uuid,$http_method,$tunnel_id/$imsi,$monitortag/$imei,$parent_session_id,$parent_start_time,$tunnel,$thr_category,$contentver,,$assoc_id,$ppid,$http_headers,$url_category_list,$rule_uuid,$http2_connection,$dynusergroup_name,$xff_ip,$src_category,$src_profile,$src_model,$src_vendor,$src_osfamily,$src_osversion,$src_host,$src_mac,$dst_category,$dst_profile,$dst_model,\$dst_vendor,$dst_osfamily,$dst_osversion,$dst_host,$dst_mac,$container_id,$pod_namespace,$pod_name,$src_edl,$dst_edl,$hostid,$serialnumber,$domain_edl,$src_dag,$dst_dag,$partial_hash,$high_res_timestamp,$reason,\$justification,$nssai_sst
,$_receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$srcuser,$vsys,$machinename,$os,$src,$matchname,$repeatcnt,$matchtype,,,$seqno,$actionflags,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name,$vsys_id,$srcipv6,$hostid,$mac,$high_res_timestamp
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$vsys,$ip,$user,$datasourcename,$eventid,$repeatcnt,$timeout,$beginport,$endport,$datasource,$datasourcetype,$seqno,$actionflags,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name,$vsys_id,$factortype,$factorcompletiontime,$factorno,,,$ugflags,$userbysource,$high_res_timestamp
,$receive_time,$serial,$type,$subtype,,$time_generated,$vsys,$ip,$user,$datasourcename,$eventid,$repeatcnt,$timeout,$beginport,$endport,$datasource,$datasourcetype,$seqno,$actionflags,$dg_hier_level_1,$dg_hier_level_2,$dg_hier_level_3,$dg_hier_level_4,$vsys_name,$device_name,$vsys_id,$factortype,$factorcompletiontime,$factorno,,,$ugflags,$userbysource
- Click OK.
- Commit the changes.
Step 3: Configure Palo Alto Firewall
In this step, you configure Palo Alto Firewall to send log messages to the Sumo Logic platform. Follow Palo Alto documentation to Configure Log Forwarding.
Step 4: Verify ingestion
In this step, you verify that your logs are successfully making it into CSE.
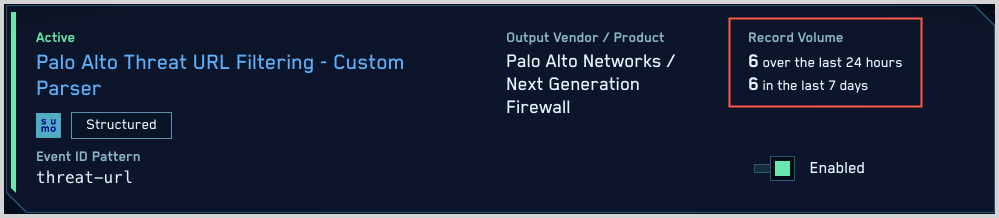
- Click the gear icon, and select Log Mappings under Incoming Data.
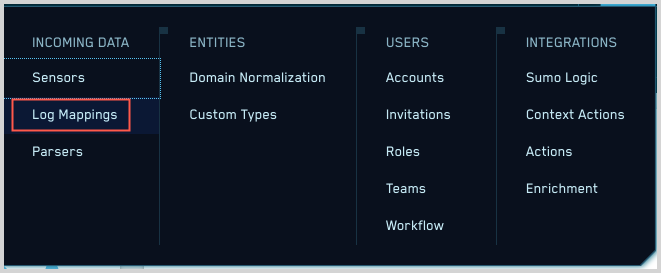
- On the Log Mappings page search for "Palo Alto" and check under Record Volume.
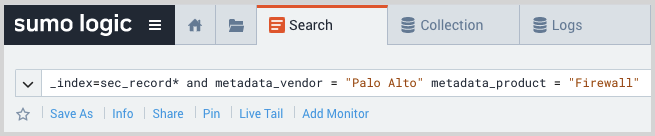
- For a more granular look at the incoming records, you can also search the Sumo Logic platform for Palo Alto Firewall security records.