Before You Deploy
This page describes prerequisites and guidelines for deploying Sumo Logic’s AWS Observability Solution.
Prerequisites
Sumo Logic Metrics. The AWS Observability Solution leverages both logs and metrics to provide comprehensive monitoring and troubleshooting of your AWS cloud infrastructure. If you do not already have Metrics, contact your Sumo Logic account representative. AWS Observability integrates with Explore by populating metadata and only shows entities with metrics coming in. If you do not see expected entities, make sure configurations are correct to collect and receive metrics including the CloudWatch Namespace for CloudFormation Template.
Sumo Logic Collectors and Sources. The AWS Observability Solution relies upon an Installed Collector with a Host Metrics Source on each of your AWS EC2 hosts. The solution relies upon host metrics collection rather than AWS CloudWatch EC2 metrics because AWS EC2 metrics from Cloudwatch have high latency and can increase the costs of your AWS account. Host metrics have the advantage of near-zero latency and more information at a lower cost. Instructions are provided in Configure Host Metric Source below.
Make sure you have access to the Sumo Logic console and as a user that is associated with Sumo Logic role and required role capabilities.
Role capabilities. Make sure you have a Sumo Logic role that have the following capabilities:
- Manage field extraction rules
- Manage connections
- View Account Overview
- View Fields
- View field extraction rules
- Manage Content
- Manage Collectors
- View Collectors
- Manage Fields
- Manage Monitors
- Manage Metrics Rules
- View Monitors
- Manage Entity Type Configs
- Create access keys
Sumo Logic Access ID and Key. When you deploy the solution, you’ll need to supply a Sumo Logic Access ID and Access Key, which enable you to use Sumo Logic APIs. Make sure you have the role capabilities listed above before generating the Access ID and Key.
AWS credentials. To deploy the solution, you will need to log onto the AWS Console. For the CloudFormation template deployment option, your AWS role must have the permissions described by this JSON file. As necessary, you may add JSON text to an existing or a new policy associated with an AWS IAM role as described in the AWS documentation. For Terraform deployment options, see the *.tmpl files in this folder aws-observability-terraform/source-module/templates/.
Set up the AWS CLI and configure the AWS CLI as described in the AWS documentation if you would like to use an AWS profile for Terraform script based deployment.
The AWS Observability solution comes with pre-packaged alerts in the form of Sumo Logic Monitors. To understand more about their capabilities please visit the Monitors page.
Deployment options
You can deploy AWS Observability to a single AWS account and region, or to all of your accounts in all regions. We provide instructions for both alternatives.
Typically you would first deploy the solution to a single AWS account and region, kick the tires, and then expand the deployment. See Deploy AWS Observability for a limited deployment. See Deploy to Multiple Accounts and Regions for a broader deployment.
You have two options for deploying:
- Deploy using an AWS CloudFormation template
- Deploy using a Terraform Script
Deployment Considerations
You deploy the solution by either running an AWS CloudFormation template or via Terraform scripts. When doing so, consider the following.
Do you already have the required sources?
When you deploy, you are given the option to create the Sumo Logic sources that the solution applications rely upon. If you have already configured those sources, you do not have to create new ones. You can just provide the URLs of the relevant Sumo Logic sources as part of the AWS CloudFormation or Terraform configuration.
If you use existing sources for the AWS Observability solution, rather than create new ones, it is not necessary to modify the existing metadata and source categories associated with the sources—the metadata that the solution depends on will be added to the sources at deployment time.
Install the solution apps once
The CloudFormation template gives you the option to install the solution apps. You should install the apps only during the first execution of the AWS CloudFormation template for a given Sumo Logic account.
The Terraform script gives you the option to install the solution apps using app-modules. You should install the apps only once with the app-modules for a given Sumo Logic account.
Bucket considerations
In the sections of the Terraform scripts or CloudFormation template that relate to creating Sumo Logic sources, you can specify an existing S3 bucket to store the logs that the source collects. If you don’t supply a bucket name, the template will create a new one. We recommend you use an existing bucket if possible.
Do you use AWS Control Tower?
If you use AWS Control Tower to manage your accounts, see the Sumo Logic-AWS Control Tower integration guide that specifically calls out how to use the AWS Observability solution to monitor AWS Control Tower managed accounts.
This integration is supported only via AWS CloudFormation.
Running the CloudFormation template from the command line
If desired, you can run the AWS CloudFormation template from the AWS CLI, using the deploy command. You can use this script, as an example.
Configure Host Metrics sources
Follow the instructions in this section to configure an Sumo Logic Installed Collector and a Host Metrics Source on each of your AWS EC2 hosts. You will assign account and Namespace metadata fields to the sources so that incoming logs and metrics will be appropriately tagged.
This step is not necessary if you already have an Installed Collector and Host Metrics tagged with account and Namespace metadata fields.
Perform these steps for each EC2 host.
- Set up an Installed Collector. For instructions, see Installed Collectors.
- Add a Host Metrics Source to the Installed Collector. For instructions, see Manually Configure a Host Metrics Source. In the Fields portion of the configuration::
- Add a field named
account, and set it to your AWS account alias. - Add a field
Namespacenamed and set it toAWS/EC2. - Set the Scan Interval (the frequency at which the Source is scanned) to 1 minute.
A default Scan Interval of 1 minute is recommended. You can set it to a higher or lower interval as needed. Faster intervals may result in increased consumption cost.
To automate the above, see Add Fields to Existing Host Metrics Sources.
Going forward, you can also build your EC2 AMI machine image with these fields and settings. For instructions, see this blog.
Here’s a sample sources.json file that you can include in your AMI.
{
"api.version": "v1",
"source": {
"name": "Host Metrics",
"category": "hostmetrics",
"automaticDateParsing": false,
"multilineProcessingEnabled": true,
"useAutolineMatching": true,
"contentType": "HostMetrics",
"forceTimeZone": false,
"filters": [],
"cutoffTimestamp": 0,
"encoding": "UTF-8",
"fields": {
"account": "<your AWS account alias>",
"Namespace": "AWS/EC2"
},
"thirdPartyRef": {
"resources": [
{
"serviceType": "HostMetrics",
"path": {
"type": "NoPathExpression"
},
"authentication": {
"type": "NoAuthentication"
}
}
]
},
"interval": 300000,
"metrics": [
"CPU_User",
"CPU_Sys",
…..
],
"processMetrics": [],
"sourceType": "SystemStats"
}
}
Verify AWS and Sumo Logic Permissions
Before setting up the AWS Observability solution we recommend testing permissions for both AWS and Sumo Logic by using a test AWS CloudFormation template. To execute this template:
Invoke the AWS CloudFormation template at this URL.
Select the desired AWS region to test.
Enter a Stack Name, Sumo Logic Deployment, and Sumo Logic Access ID and Access Key.
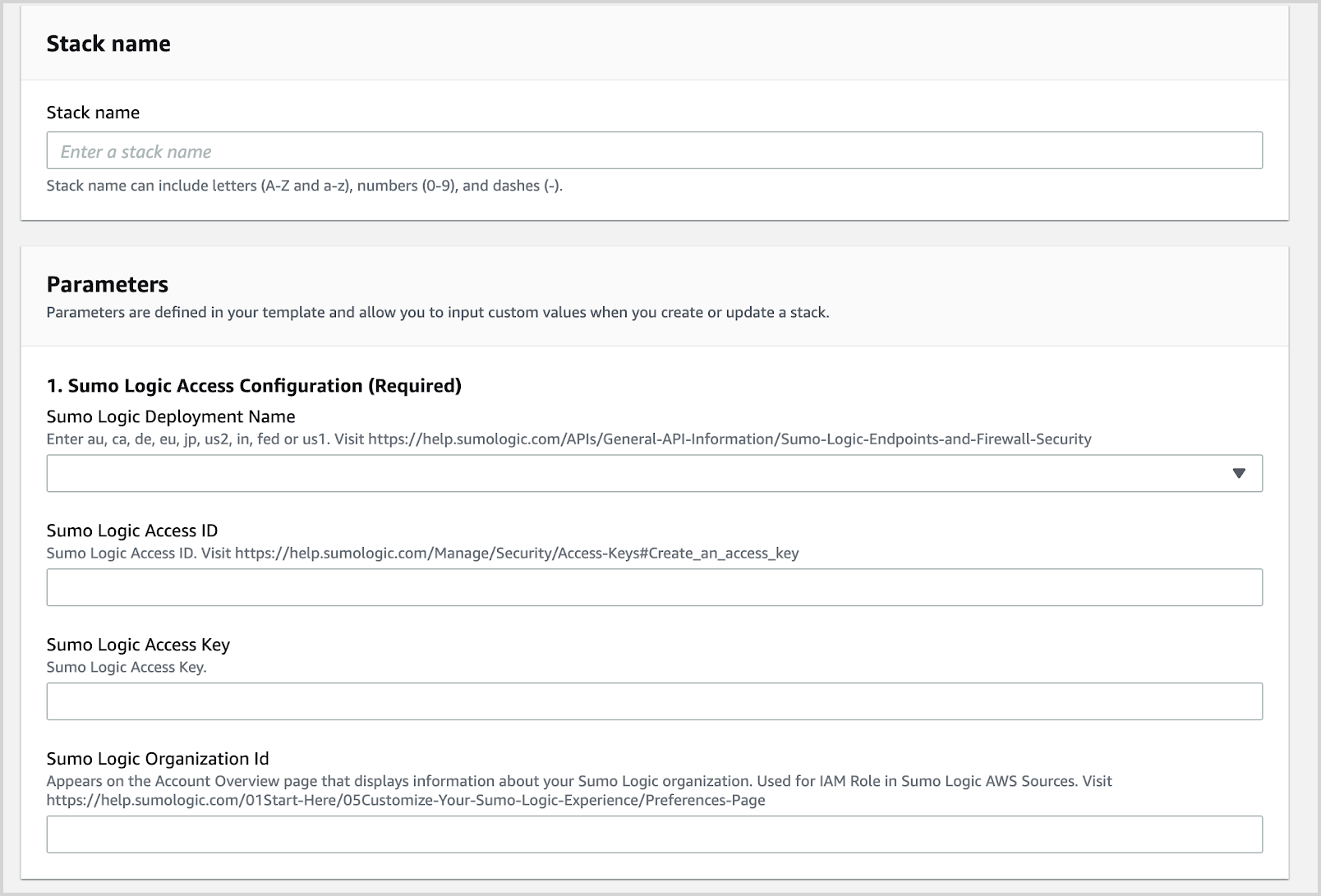
Click Create Stack.
Verify that the AWS CloudFormation template has executed successfully in a CREATE_COMPLETE status.
- This indicates that you have all the right permissions on both the Sumo Logic and the AWS side to proceed with the installation of the solution.
- All the resources (Sumo Logic and AWS) created by template are also deleted.
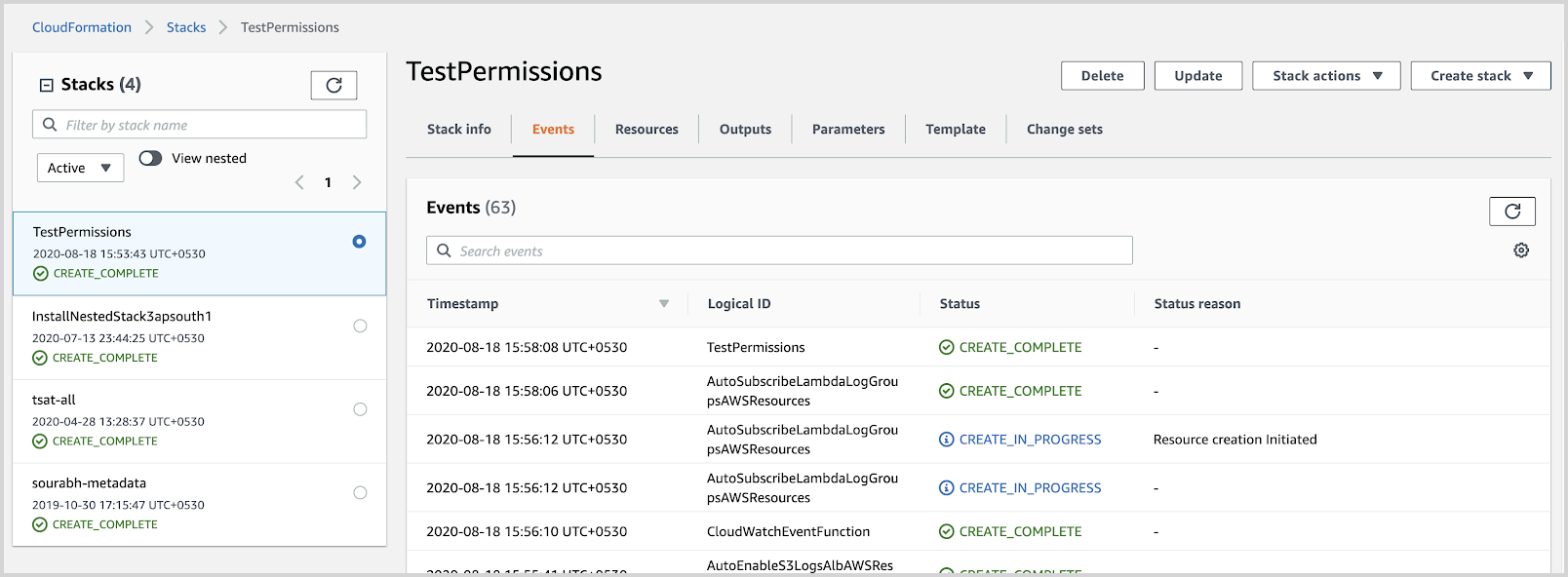
If the AWS CloudFormation template has not executed successfully, identify and fix any permission errors till the stack completes with a CREATE_COMPLETE status.
Once the AWS CloudFormation stack has executed successfully, delete the AWS CloudFormation Stack.

