Cybereason Source
The Cybereason Source provides a secure endpoint to receive authentication logs from the Cybereason Malops API. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
The Cybereason API documentation is not public and can only be accessed by partners or customers.
If you want to explicitly allow the static IP addresses used for this Source on Cybereason see our table of static IP addresses by deployment.
States
A Cybereason Source tracks errors, reports its health, and start-up progress. You’re informed, in real-time, if the Source is having trouble connecting, if there's an error requiring user action, or if it is healthy and collecting by utilizing Health Events.
A Cybereason Source goes through the following states when created:
- Pending: Once the Source is submitted it is validated, stored, and placed in a Pending state.
- Started: A collection task is created on the Hosted Collector.
- Initialized: The task configuration is complete in Sumo Logic.
- Authenticated: The Source successfully authenticated with Cybereason.
- Collecting: The Source is actively collecting data from Cybereason.
If the Source has any issues during any one of these states it is placed in an Error state.
When you delete the Source it is placed in a Stopping state, when it has successfully stopped it is deleted from your Hosted Collector.
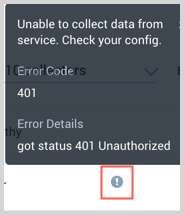
On the Collection page, the Health and Status for Sources is displayed. Use Health Events to investigate issues with collection. You can click the text in the Health column, such as Error, to open the issue in Health Events to investigate.
Hover your mouse over the status icon to view a tooltip with details on the detected issue.
Authentication
You need to have a Cybereason username and password as well as your customer-specific host, such as mydomain.cybereason.net. If you have a customer-specific port this should be included, such as mydomain.cybereason.net:8443.
Create a Cybereason Source
When you create a Cybereason Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Configure a Hosted Collector.
To configure a Cybereason Source:
In Sumo Logic, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a Hosted Collector.
Select Cybereason.
Enter a Name to display for the Source in the Sumo web application. The description is optional.
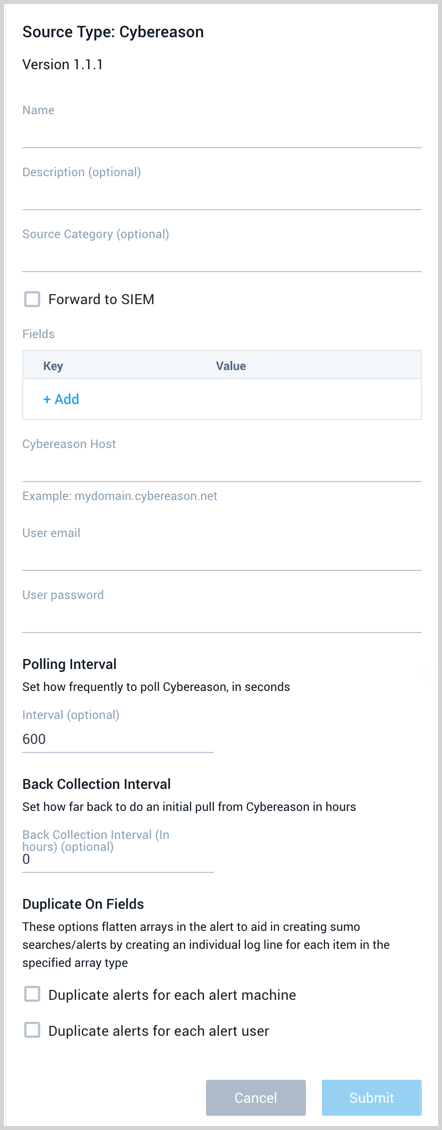
(Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory.Forward to SIEM. Check the checkbox to forward your data to Cloud SIEM Enterprise. When configured with the Forward to SIEM option the following metadata fields are set:
_siemVendor: Cybereason_siemProduct: Endpoint Security_siemFormat: JSON_siemEventID:<eventType>Whereevent_typeis the value of the field malopDetectionType from the JSON event.
(Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate, each field needs a name (key) and value.
A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored, known as dropped.
Cybereason Host. Provide your customer-specific host, such as
mydomain.cybereason.net. If you have a customer-specific port this should be included, such asmydomain.cybereason.net:8443.User email and password. Provide the Cybereason user credentials you want to use to authenticate collection requests.
(Optional) The Polling Interval is set for 300 seconds by default, you can adjust it based on your needs. This sets how often the Source checks for new data.
(Optional) The Back Collection Interval allows you to set, in hours, ingestion for up to 30 days of prior MalOps.
(Optional) Duplicate On Fields, when enabled, each value in the array of machines or users is put into its own log. The entire log is duplicated for each value in the array, where each log gets one value. For example,
{
"data": 1,
"machine": [1, 2, 3]
}Would be processed into three logs, each with a single value from the machine array, like this:
{
"data": 1,
"machine": 1
}
{
"data": 1,
"machine": 2
}
{
"data": 1,
"machine": 3
}When you are finished configuring the Source click Submit.
Error types
When Sumo Logic detects an issue it is tracked by Health Events. The following table shows the three possible error types, the reason the error would occur, if the Source attempts to retry, and the name of the event log in the Health Event Index.
| Type | Reason | Retries | Retry Behavior | Health Event Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThirdPartyConfig | Normally due to an invalid configuration. You'll need to review your Source configuration and make an update. | No retries are attempted until the Source is updated. | Not applicable | ThirdPartyConfigError |
| ThirdPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the third party service APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which retries will be attempted every 60 minutes. | ThirdPartyGenericError |
| FirstPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the internal Sumo Logic APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which retries will be attempted every 60 minutes. | FirstPartyGenericError |
JSON configuration
Sources can be configured using UTF-8 encoded JSON files with the Collector Management API. See how to use JSON to configure Sources for details.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config | JSON Object | Yes | Contains the configuration parameters for the Source. | |
| schemaRef | JSON Object | Yes | Use {"type":"Cybereason"} for a Cybereason Source. | not modifiable |
| sourceType | String | Yes | Use Universal for a Cybereason Source. | not modifiable |
The following table shows the config parameters for a Cybereason Source.
| Parameter | Type | Required? | Default | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
name | String | Yes | Type a desired name of the Source. The name must be unique per Collector. This value is assigned to the metadata field _source. | modifiable | |
description | String | No | null | Type a description of the Source. | modifiable |
category | String | No | null | Type a category of the source. This value is assigned to the metadata field _sourceCategory. See best practices for details. | modifiable |
fields | JSON Object | No | JSON map of key-value fields (metadata) to apply to the Collector or Source. Use the boolean field _siemForward to enable forwarding to SIEM. | modifiable | |
client_user | String | Yes | Provide the email address you want to use to authenticate collection requests. | modifiable | |
client_password | String | Yes | Provide the password for the user that you want to use to authenticate collection requests. | modifiable | |
polling_interval | Integer | No | 300 | This sets how often the Source checks for new data. | modifiable |
back_collection_hours | Integer | No | 0 | Sets the number of hours of prior MalOps to collect. Supports 0 to 720. | modifiable |
dup_machines | Boolean | No | False | Set to true to duplicate logs for each element in the machine array. | modifiable |
dup_users | Boolean | No | False | Set to true to duplicate logs for each element in the users array. | modifiable |
Cybereason Source JSON example:
{
"api.version":"v1",
"source":{
"schemaRef":{
"type":"Cybereason"
},
"config":{
"back_collection_hours":720,
"name":"test cybereason",
"domain":"mydomain.cybereason.net",
"client_password":"********",
"polling_interval":300,
"fields":{
"_siemForward":false
},
"dup_users":true,
"category":"c2c/cybereason",
"client_user":"********"
},
"state":{
"state":"Collecting"
},
"sourceType":"Universal"
}

