Preconfigure a Machine to Collect Remote Windows Events
Use the instructions in this topic to configure a system for remote access by a Remote Windows Event Log Source. For information on collecting local Windows Event Logs, see Configure a Local Windows Event Log Source.
Windows events can only be collected, locally or remotely, from systems running Windows Server 2012 or later.
There are two primary configuration requirements to enable remote event log collection:
- The user account specified in the source must have permissions to read the event log remotely
- The firewall on the remote machine must be configured to allow inbound connections for reading the event log
User account
When configuring the Source, you will enter a domain name, user name, and password. This user account will be used by the Collector to perform the remote collection of event log records. The credentials are stored in Sumo's database encrypted and in the Collector's memory. The account must be configured such that it has permissions to read the event log from each of the specified remote systems.

An account has permissions to read events remotely if it is either a local Administrator or a member of the Event Log Readers local group on the target system. As a security best practice, it is recommended that a non-administrator account is used.
UI
Open the Computer Management app (compmgmt.msc)
Navigate to Local Users and Groups, and select Groups.
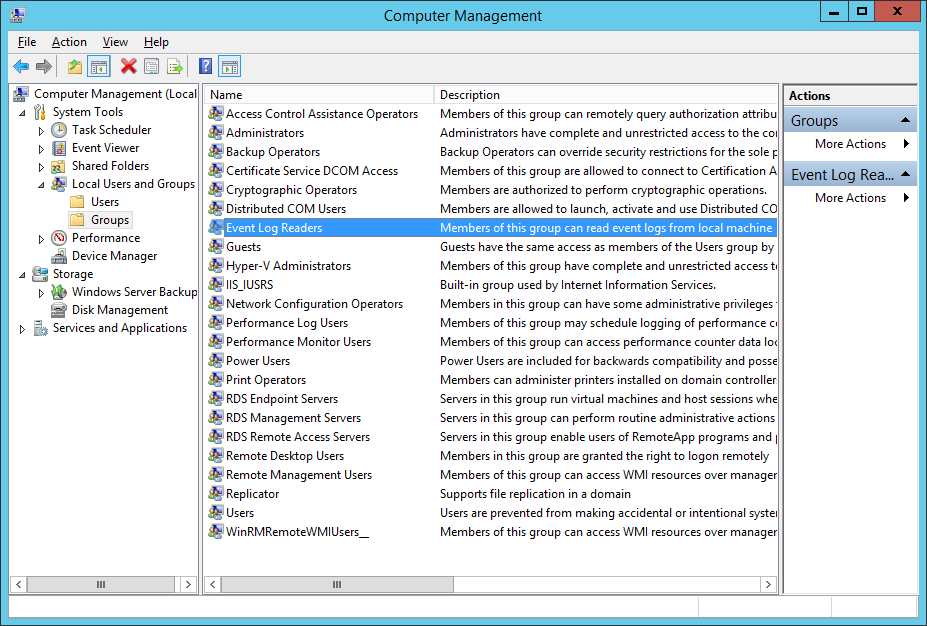
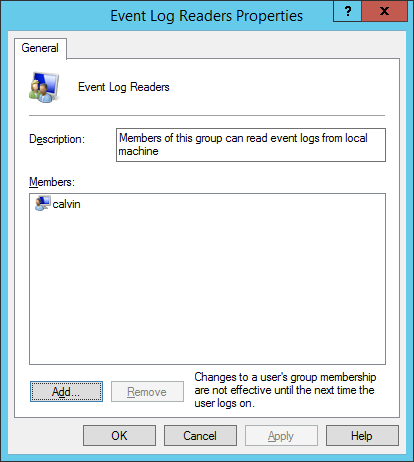
Double-click on the Event Log Readers group, and add the account as a new member.
Command line
A user can be added to the Event Log Readers local group using the following command line:
net localgroup "Event Log Readers" <domain\username> /add
Firewall configuration
To allow for remote systems to read the Windows event log, a set of inbound firewall exceptions must be enabled.
UI
- Open the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security app (wf.msc).
- On the left panel, select Inbound Rules
- Scroll down to the set of rules named Remote Event Log Management. Enable all of the Remote Event Log Management rules, to permit inbound traffic.
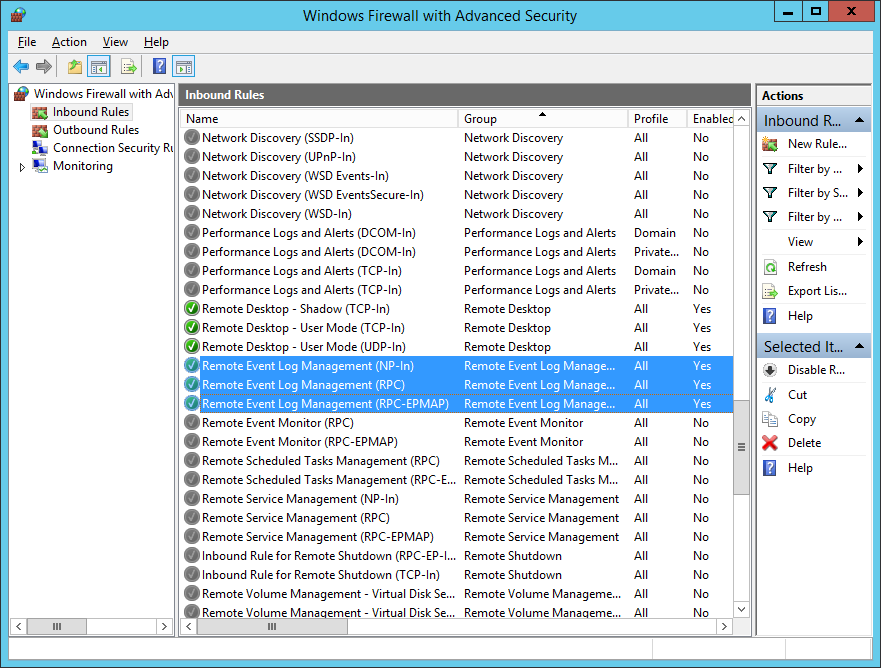
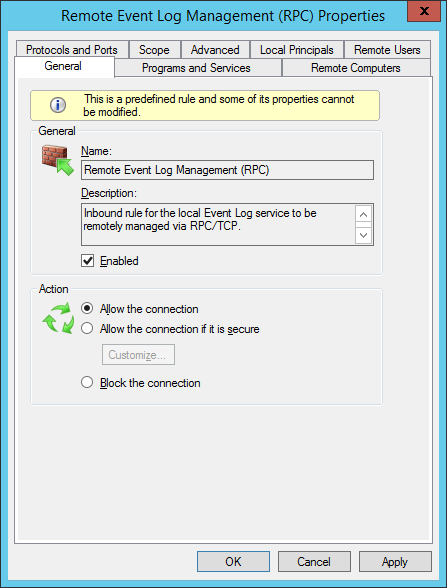
For each of these firewall rules, you can do fine-grained scoping to allow traffic only from domain systems, only from particular accounts, only from certain IP ranges, and so forth. Appropriate settings will depend on your organization's IT infrastructure and security policies.
Command Line
You can configure firewall rules from the command line with the netsh command:
rem Enables all rules in the Remote Event Log Management group, for all network profiles
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group="Remote Event Log Management" new enable=yes
netsh also supports fine-grained firewall configuration. For details on these parameters, see the netsh advfirewall documentation.

