along
The along operator joins metric queries to have Sumo evaluate and perform expressions by comparing one or more metric fields. It considers multiple query rows and metrics referenced by another row according to one field or multiple fields separated by a comma (#A, #B,...).
along is helpful in the following usage:
- Simple row references (#A to #F) with math expressions. For example:
#A * 100Math expressions support the same set of functions as the eval operator so you can use sin, cos, abs, log, round, ceil, floor, tan, exp, sqrt, min, and max. - Evaluate multiple metrics. A single row can contain references to multiple rows, comparing metrics by joining them together in another row, or to to filter results of a query (row) by metadata from another row. For example:
#C: #B - #A along _sourceHost
We recommend using along to refine your queries when comparing and using data from multiple queries. Otherwise, you will receive many-to-many relations.
Using RowID in Queries
With these operators, you can execute multiple queries (up to 6 from A to F) and use that rowID to compare multiple queries in the same line or chart.
The rowID is the lettered query you created. Use it to get information on multiple metrics for the same desired time series. For example, you may want to plot out a CPU, Memory, and Disk metric all on one chart (same time series). Include three metric queries for A, B, and C. You can also use join with the along operator using rowIDs.
Use the lettered query (#A, #B, #C, …) for every request where there is only one metric query. Based on the response on rowID, you increment to B, C, D, E, and F (up to 6 queries) if you want multiple related metric queries returned for a single time series.
along syntax
#A + #B along [FIELD (,FIELD, ...]]
```
## along examples
### Summation for a time series
This query performs a summation for time series whose dimension value matches. For example, you could use `_sourceHost` as the dimension, ensuring a time series in row A is only added with a time series in row B if they have the same `_sourceHost`.
```sql
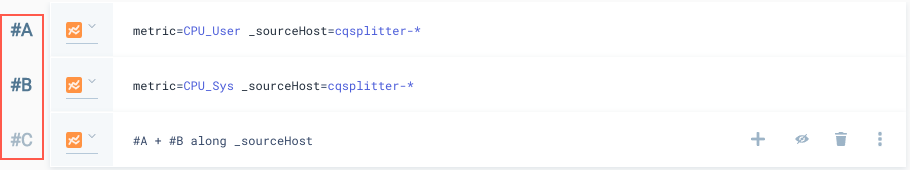
metric=CPU_User _sourceHost=cqsplitter-*
metric=CPU_Sys _sourceHost=cqsplitter-*
#A + #B along _sourceHost
Disk percent between available and free by device name
This query considers and returns a disk percentage metric available and free for devices where the device name matches.
(#B / (#A + #B)) * 100 as DiskUsedPercent along DevName
Sum and create a total metric
This query adds bytes_in with bytes_out for each node, and creates the metric bytes_total. Each time-series in A gets paired with an appropriate series from B, the one that has the same cluster and node fields. along specifies this pairing.
Row C: #A + #B along cluster, node as bytes_total
metric=bytes_total, node=node-1, cluster=search C1 = A1 + B1
metric=bytes_total, node=node-2, cluster=search C2 = A2 + B2
metric=bytes_total, node=node-1, cluster=metrics C3 = A3 + B3
Calculate percentages for nodes by cluster
This query calculates bytes_in as a percentage of bytes_total on each node. The expression allows referring to the same series more than once in the expression: #A appears twice in the expression.
Row C: #A * 100 / (#A + #B) along cluster, node as bytes_in_pct_total
metric=bytes_in_pct_total, node=node-1, cluster=search C1 = A1 * 100 / (A1 + B1)
metric=bytes_in_pct_total, node=node-2, cluster=search C2 = A2 * 100 / (A2 + B2)
metric=bytes_in_pct_total, node=node-1, cluster=metrics C3 = A3 * 100 / (A3 + B3)
Simulate metadata filtering
This query simulates the effect of filtering on metadata from a row by using metrics joins expressions that remove the data part from that row. The following example effectively filters results from row B to those with _``sourcehosts in row A.
#B + 0 *#A along _sourceHost
An advanced version of this query shows all metrics of CPU_LoadAvg for 1 minute, 5 minutes, and 15 minutes for three servers which have maximum load_avg.one:
A: _sourceHost=nite-metricsstore-* CPU_LoadAvg_1min | topk(3,avg)
B: _sourceHost=nite-metricsstore-* CPU_LoadAvg_5min
C: _sourceHost=nite-metricsstore-* CPU_LoadAvg_15min
D: (#B + 0 * #A) along _sourceHost
E: (#C + 0 * #A) along _sourceHost
Queries with aggregate operator
When running a join queries with aggregate operator:
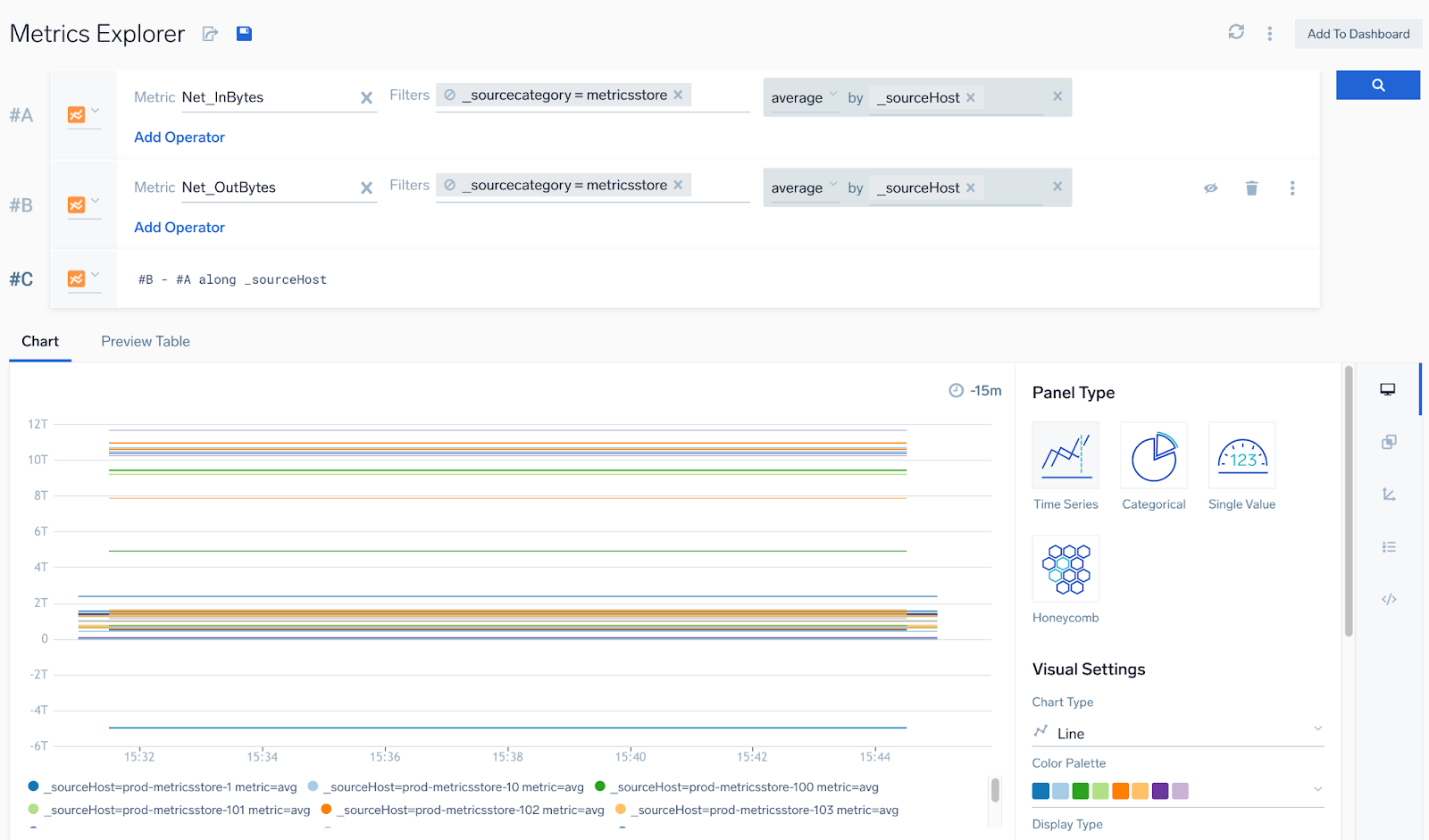
#A: metric=Net_InBytes | avg by _sourceHost
#B: metric=Net_OutBytes | avg by _sourceHost
Include the aggregation dimension in the result query using along operator:
#C: #B - #A along _sourceHost