MS Graph Azure AD Reporting Source
The Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source collects Directory Audit, Sign-in, and Provisioning data from the Microsoft Graph API Azure AD activity reports. It securely stores the required authentication, scheduling, and state tracking information.
Data is polled every five minutes and can take a couple of minutes to be searchable in Sumo Logic.
If you want to explicitly allow the static IP addresses used for this Source on your firewall see our table of static IP addresses by deployment.
States
A Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source tracks errors, reports its health, and start-up progress. You’re informed, in real-time, if the Source is having trouble connecting, if there's an error requiring user action, or if it is healthy and collecting by utilizing Health Events.
A Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source goes through the following states when created:
- Pending: Once the Source is submitted it is validated, stored, and placed in a Pending state.
- Started: A collection task is created on the Hosted Collector.
- Initialized: The task configuration is complete in Sumo Logic.
- Authenticated: The Source successfully authenticated with Microsoft.
- Collecting: The Source is actively collecting data from Microsoft.
If the Source has any issues during any one of these states it is placed in an Error state.
When you delete the Source it is placed in a Stopping state, when it has successfully stopped it is deleted from your Hosted Collector.
On the Collection page, the Health and Status for Sources is displayed. Use Health Events to investigate issues with collection. You can click the text in the Health column, such as Error, to open the issue in Health Events to investigate.
Hover your mouse over the status icon to view a tooltip with a count of the detected errors and warnings.
![]()
You can click on the status icon to open a Health Events panel with details on each detected issue.
Set up a Service Application
The Source requires the creation and registration of a service application within the Azure Active Directory portal.
The user creating the service application does not need to be an administrator. However, an administrator is needed to grant the application the appropriate permissions to the Activity Reports API.
Use the following steps to create a service application:
Log in to the Azure Active Directory Portal
Then select Azure Active Directory in the left menu.
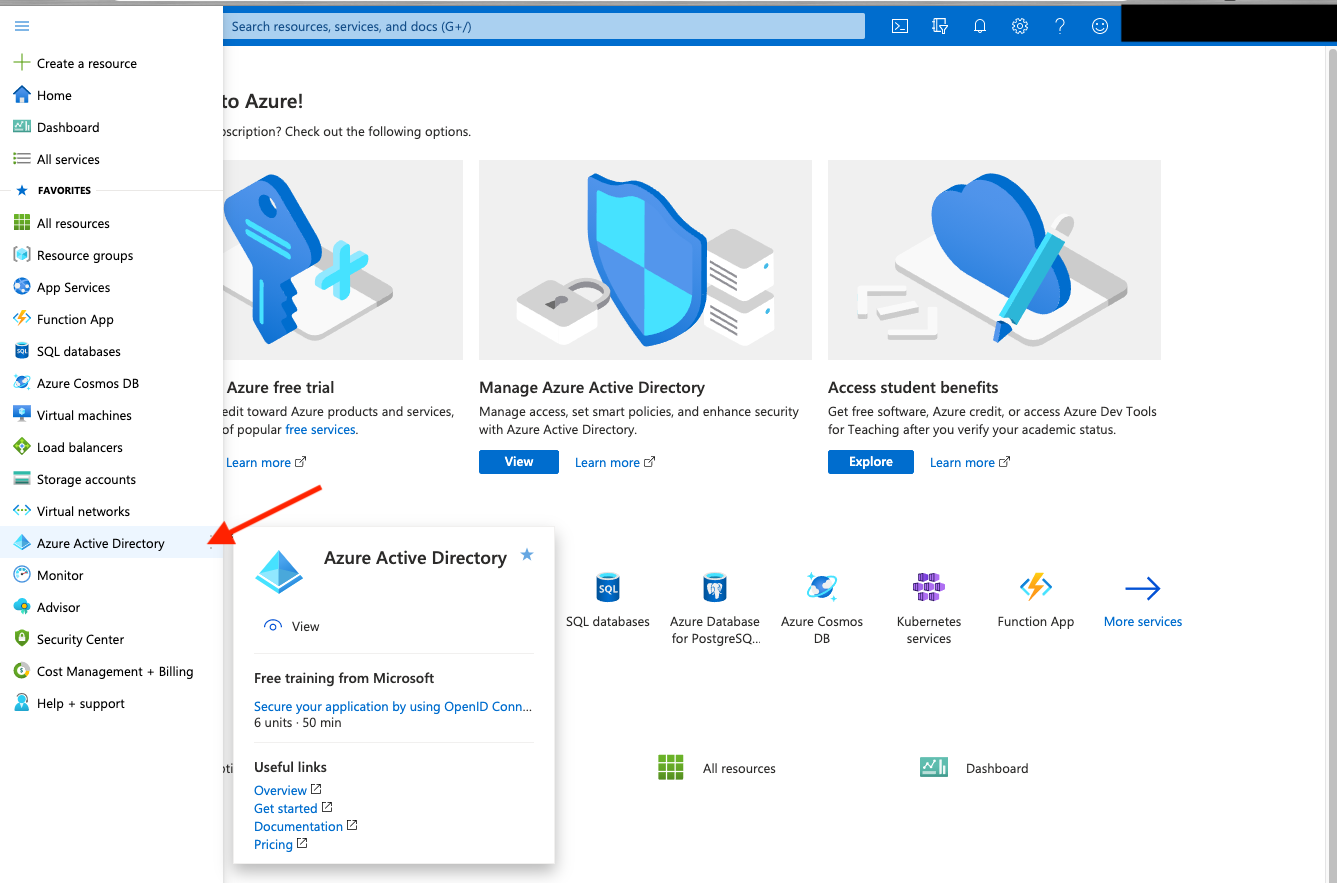
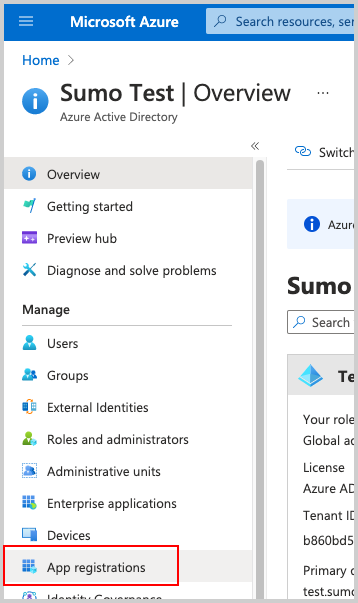
Then select App Registrations.
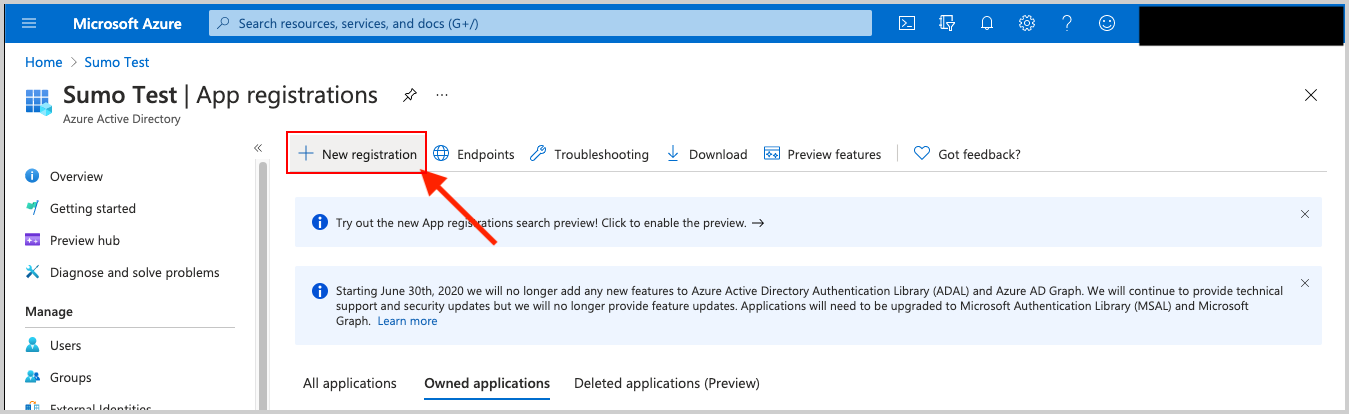
Then select New Registration. Go through the registration process, providing a name for the application. Selecting Accounts in this organizational directory only is sufficient.
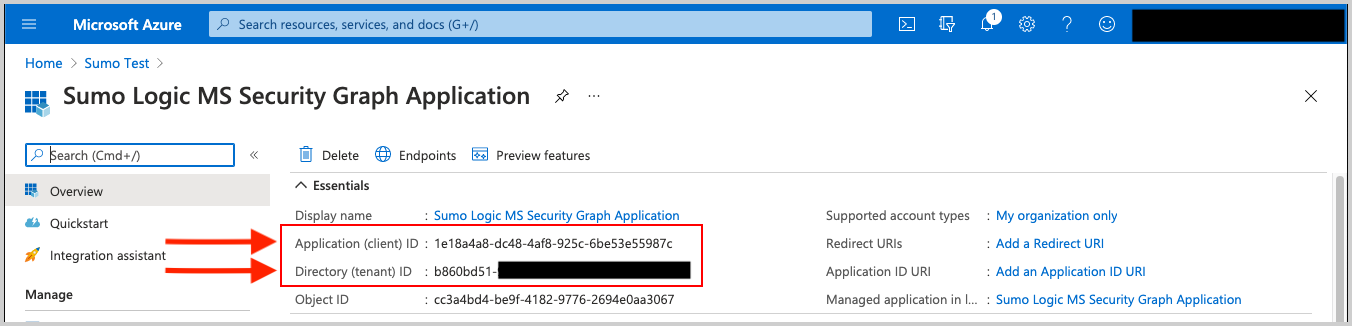
After the Application is registered (created), be sure to copy the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID. These are used later as configuration parameters in Sumo Logic when creating the Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source.
Within the Application configuration page, select Certificates and Secrets to create an Application Client Secret Key.
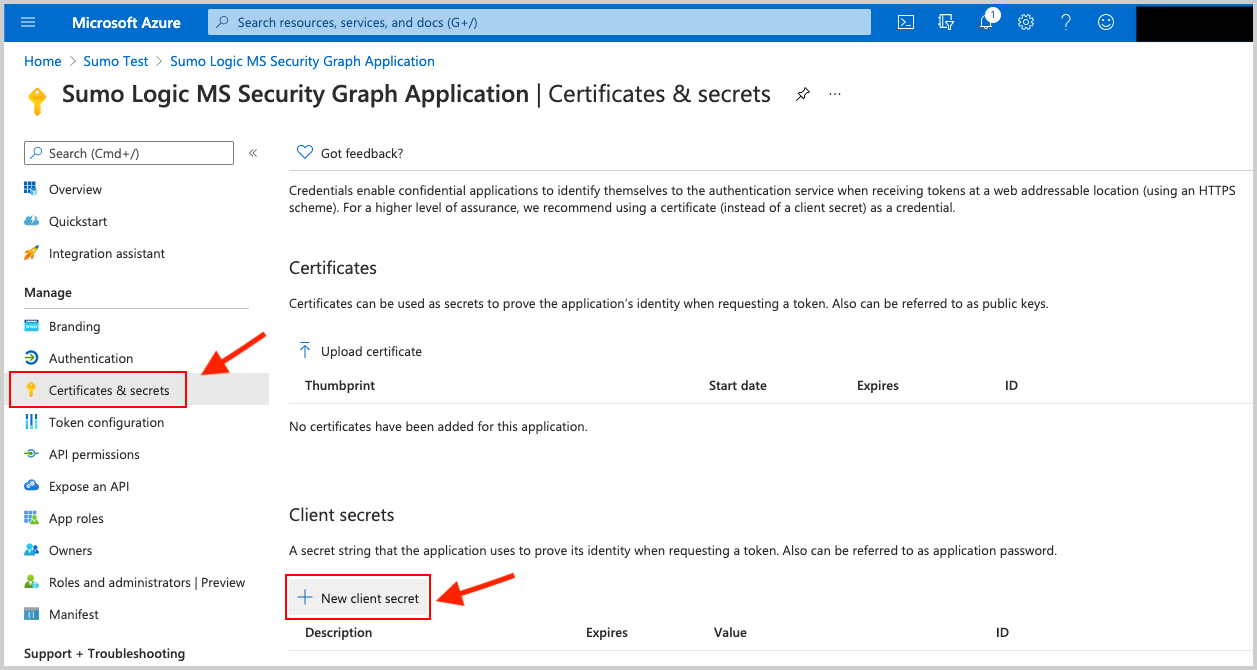
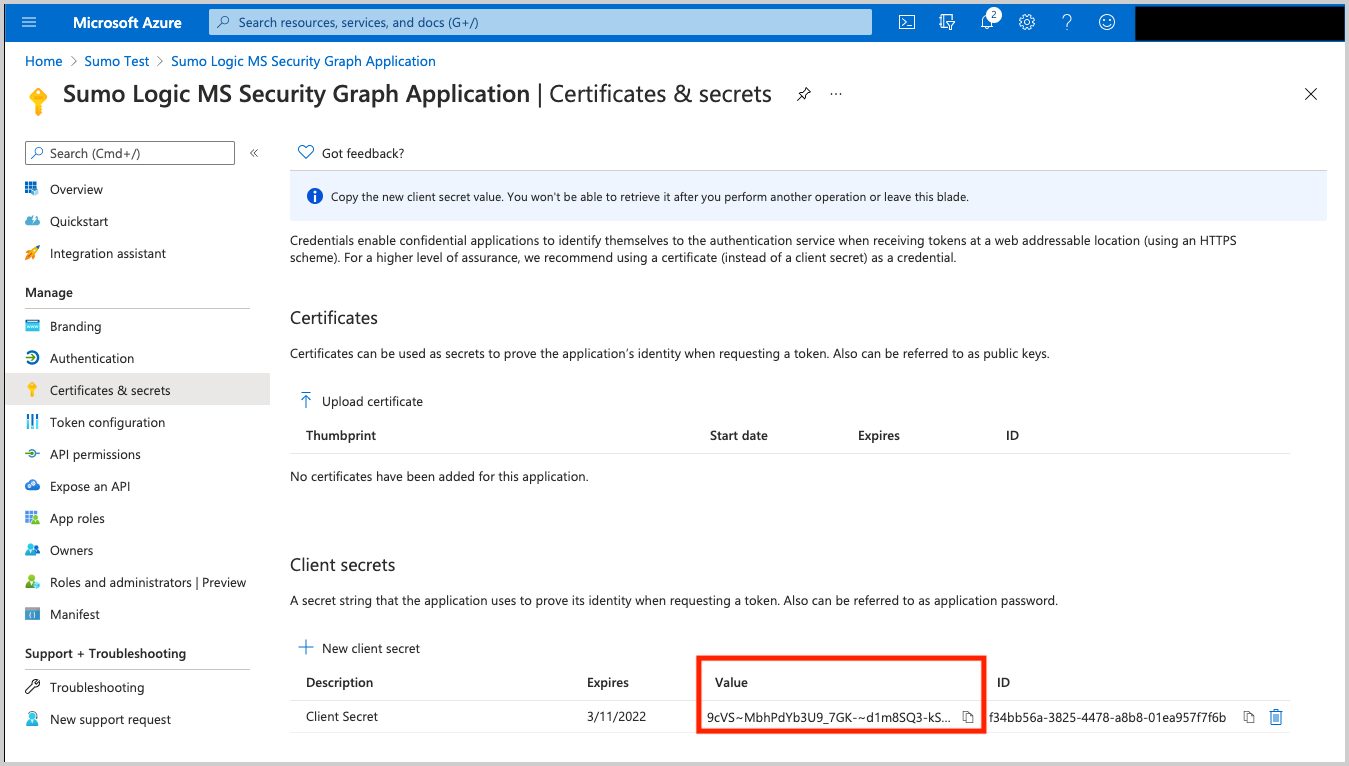
Copy the Client Secret Value (pictured below). It's needed later in Sumo Logic when creating the Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source.
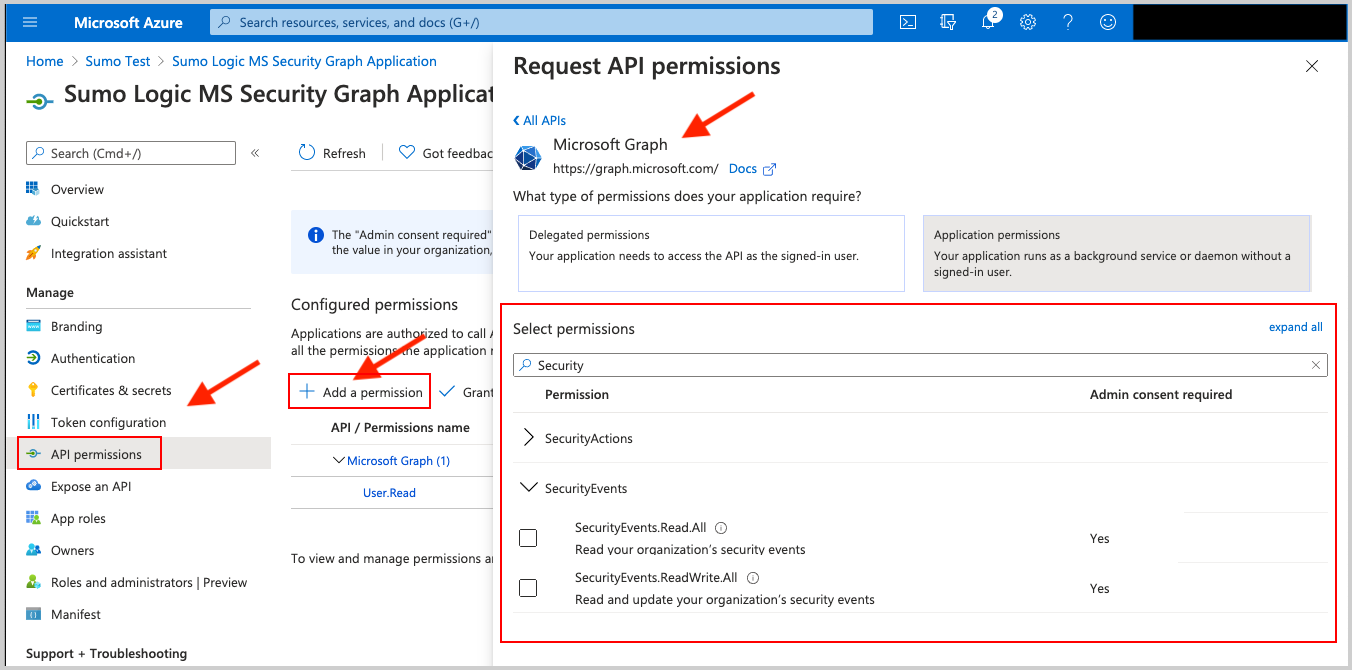
Request the appropriate permissions for the application. Click on API Permissions, then Add a permission and select Microsoft Graph. From there select (or search for) the following permissions. An Administrator must approve (grant) these permissions before the integration will function.
| API | Account Type | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Directory Audit | Delegated (work or school account) | AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read.All |
| Directory Audit | Delegated (personal Microsoft account) | Not supported. |
| Directory Audit | Application | AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read.All |
| Sign-in | Delegated (work or school account) | AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read.All |
| Sign-in | Delegated (personal Microsoft account) | Not supported. |
| Sign-in | Application | AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read.All |
| Provisioning | Delegated (work or school account) | AuditLog.Read.All and Directory.Read.All |
| Provisioning | Delegated (personal Microsoft account) | Not supported. |
| Provisioning | Application | AuditLog.Read.All |
Create a Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source
When you create a Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source, you add it to a Hosted Collector. Before creating the Source, identify the Hosted Collector you want to use or create a new Hosted Collector. For instructions, see Create a Hosted Collector.
To configure a Microsoft Graph Azure AD Reporting Source:
In the Sumo Logic web app, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
On the Collectors page, click Add Source next to a Hosted Collector.
Select MS Graph Azure AD Reporting.

Enter a Name to display for the Source in the Sumo web application. The description is optional.
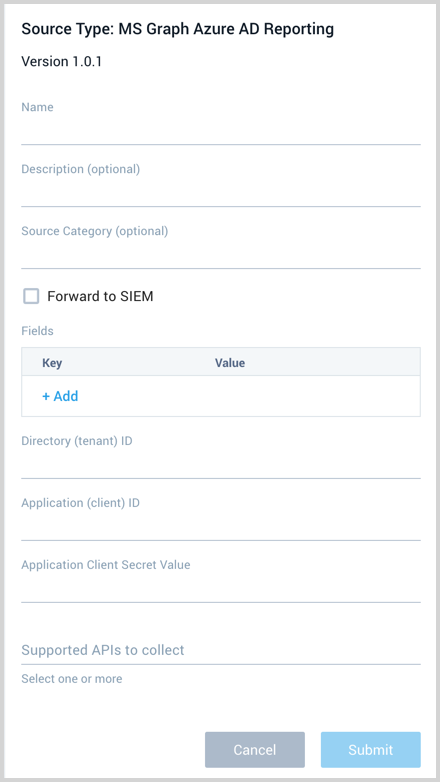
(Optional) For Source Category, enter any string to tag the output collected from the Source. Category metadata is stored in a searchable field called
_sourceCategory.Forward to SIEM. Check the checkbox to forward your data to Cloud SIEM Enterprise. When configured with the Forward to SIEM option the following metadata fields are set:
_siemVendor: Microsoft_siemProduct: Graph AD Reporting API_siemFormat: JSON_siemEventID: The _siemEventId is set to the type of data ingested. Possible values are:- Directory audit:
directoryAudits-{{activityDisplayName}} - Provisioning:
provisioning-{{provisioningAction}} - Sign-in:
signin-{{status.errorCode}}
- Directory audit:
(Optional) Fields. Click the +Add Field link to define the fields you want to associate, each field needs a name (key) and value.
A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists in the Fields table schema.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist in the Fields table schema. In this case, an option to automatically add the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema is provided. If a field is sent to Sumo that does not exist in the Fields schema it is ignored, known as dropped.
Provide the Directory (tenant) ID and Application (client) ID you got after you registered (created) the Azure Application in step 5 of the setup section.
Application Client Secret Value. Provide the Application Client Secret Value you created in step 7 of the setup section.
Supported APIs to collect. Select one or more of the available APIs: Directory Audit, Sign-in, and Provisioning.
When you are finished configuring the Source click Submit.
Error types
When Sumo Logic detects an issue it is tracked by Health Events. The following table shows the three possible error types, the reason the error would occur, if the Source attempts to retry, and the name of the event log in the Health Event Index.
| Type | Reason | Retries | Retry Behavior | Health Event Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ThirdPartyConfig | Normally due to an invalid configuration. You'll need to review your Source configuration and make an update. | No retries are attempted until the Source is updated. | Not applicable | ThirdPartyConfigError |
| ThirdPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the third party service APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | ThirdPartyGenericError |
| FirstPartyGeneric | Normally due to an error communicating with the internal Sumo Logic APIs. | Yes | The Source will retry for up to 90 minutes, after which it quits. | FirstPartyGenericError |
JSON configuration
Sources can be configured using UTF-8 encoded JSON files with the Collector Management API. See how to use JSON to configure Sources for details.
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description | Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| config | JSON Object | Yes | Contains the configuration parameters for the Source. | |
| schemaRef | JSON Object | Yes | Set to {"type":"MS Graph Azure AD Reporting"}. | not modifiable |
| sourceType | String | Yes | Set to Universal. | not modifiable |
The following table shows the config parameters for a Microsoft Graph Azure AD Source.
| Parameter | Type | Required? | Default | Description | Access ||--|--|--|--|--|--|
| name | String | Yes | | Type a desired name of the Source. The name must be unique per Collector. This value is assigned to the metadata field _source. | modifiable |
| description | String | No | null | Type a description of the Source. | modifiable |
| category | String | No | null | Type a category of the source. This value is assigned to the metadata field _sourceCategory. See best practices for details. | modifiable |
| fields | JSON Object | No | | JSON map of key-value fields (metadata) to apply to the Collector or Source. Use the boolean field _siemForward to enable forwarding to SIEM. | modifiable |
| tenant_id | String | Yes | | Provide the Directory (tenant) ID you got after you registered (created) the Azure Application. | modifiable |
| secret_key | String | Yes | | Provide the Application Client Secret Value you created in Azure. | modifiable |
| application_id | String | Yes | | Provide the Application (client) ID you got after you registered (created) the Azure Application. | modifiable |
| supported_apis | Array of strings | Yes | | Define one or more of the available APIs to collect: Directory Audit, Sign-in, and Provisioning. For example, for both you'd use: ["Directory Audit","Signin"] | modifiable |
Microsoft Graph Azure AD Source JSON example:
{
"api.version":"v1",
"source":{
"config":{
"name":"ms-azure-ad-reporting-test",
"tenant_id":"c9b18390-9cd7-4f5f-bfa5-46a50fef83f9",
"supported_apis":["Directory Audit","Signin","Provisioning"],
"secret_key":"********",
"fields":{
"_siemForward":false
},
"application_id":"5a03f2a8-4de9-4243-9d27-32c8f3921466"
},
"schemaRef":{
"type":"MS Graph Azure AD Reporting"
},
"sourceType":"Universal"
}
}