Create CSE Context Actions
This topic has information about CSE Context Actions and how to create them.
About Context Actions
A Context Action is an option that a CSE analyst can use to query an external system for information about an Entity, IOC, or data encountered in a Record. For example, you might want to check an IP address against a threat intel service, google a username, or run a log search in Sumo Logic for a hostname.
An authorized user can configure Context Actions and assign them to particular Entity types, Record fields, or common IOC types.
- Context Actions on Entity types. You can assign a Context Action to one or more Entity types, including custom Entity types. An action assigned to an Entity type will be available on any instance of that type in the Entities page, or in Insights or Signals that contain Entities of the selected type. For an example, see the screenshot in How a user accesses Contact Actions. An action you assign to an Entity type will also be available for Record fields that contain the Entity type. For example, an action assigned to the Hostname Entity type will be available for the
srcDevice_hostname,dstDevice_hostname, anddevice_hostnameRecord fields. - Context Actions on Record fields. You can assign a Context Action to selected Record fields, or all Record fields. In the CSE UI, the action will be available on the Context Action menu for selected fields.
- Context Actions on IOC Types. You can assign a Context Action
can be assigned to one or more of the following IOC data types:
- Domain
- IP Address
- URL
- Hash
- MAC Address
The Context Actions menu will be available for any of these types, wherever they appear in the CSE UI.
How a user accesses Context Actions
A user runs a Context Action by clicking the Context Action icon next to an Entity, Record field, or IOC and choosing an action from the list that appears. The icon appears when you hover over the value of the item.
In the screenshot below, Context Actions are listed below the built-in Add to Match List and Add to Suppressed List options.
![]()
If an action name is shown in red font, that indicates that the action depends on a Record field that doesn’t exist.
Configure a Context Action
Click the gear icon and the top of the CSE UI and choose Context Actions under Integrations.
On the Context Actions page click Create.
This annotated screenshot shows a previously configured Context Action in edit mode.
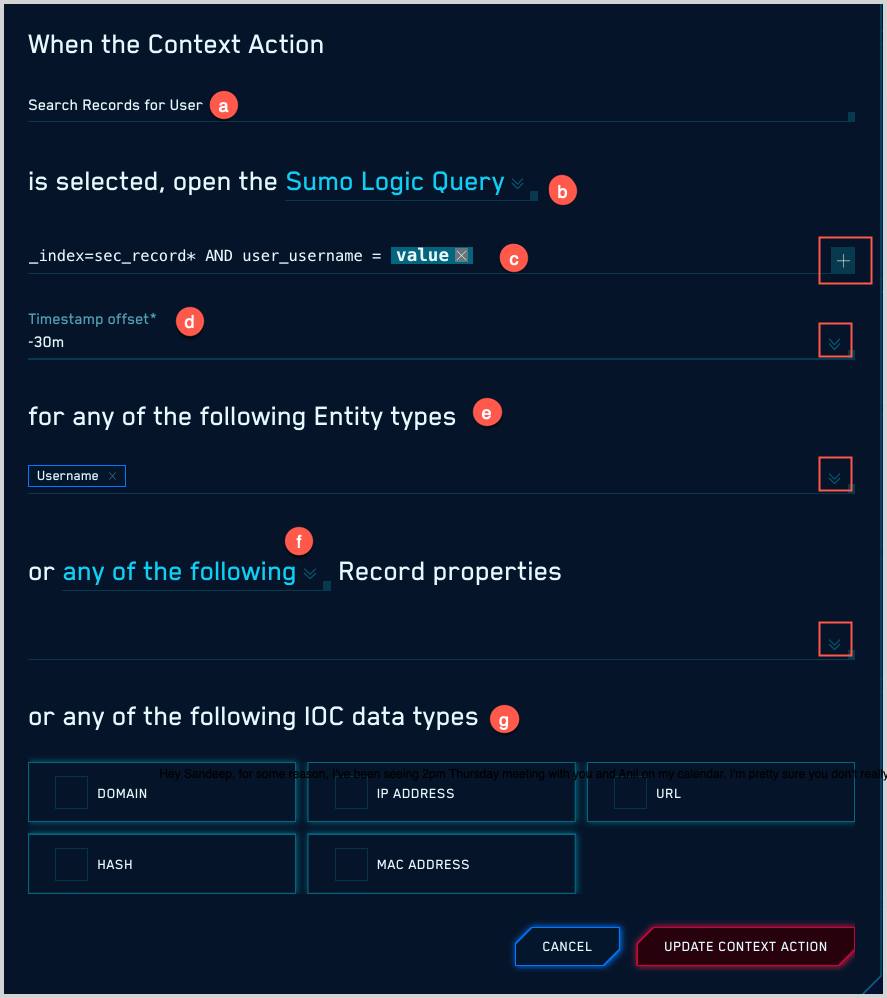
- Name. Enter a name for the Context Action.
- Choose whether you want to open a URL to an external service or a Sumo Logic Query.
- Enter the URL or log query that the Context Action will issue. For instructions, see:
- If you chose Sumo Logic Query above, the Timestamp offset option appears, which set the query time range. The offset can be either -30m or +30m, and it will be applied to the timestamp in the target Record’s timestamp field.
- Choose the Entity types to which the Context Action will apply. Use the pulldown to display a list of built-in Entity types, and any custom Entity types defined in your environment. Your Context Action will be available for any Entities of the type or types you select.
- Hostname
- IP address
- Username
- MAC Address
- Custom Entity type
- Choose the Record properties to which the Context Action will apply. You can select one or more Record fields. Your Context Action will be available for any occurrences of the fields you select.
- Choose the IOC data types to which the Context Action will apply. You can select one or more of the following data types listed below. Your Context Action will be available for any occurrences of the IOCs you select.
- Domain
- IP Address
- URL
- Hash
- MAC Address
Create a Sumo Logic search URL
To create an URL for a Sumo Logic search, you enter a Sumo Logic search query as you would in a Sumo Logic search tab, but use the {{value}} parameter placeholder for the target item. For example, for a Context Action whose target is Username, you could enter the following query to search for CSE Records of any type whose user_username field matches the username on which you run the action.
_index=sec_record* AND user_username = "{{value}}"
When you save the action, the URL template will be populated with your Sumo Logic base URL, and the time range you selected, either -30m or +30m.
{{sumobaseurl}}/ui/#/search/@{{timestamp[ms]-30m}}@_index=sec_record* AND user_username = {{value}}
Create an URL to an external service
To create a URL to be sent to an external service, enter the URL in the format required by the external service, and use the {{value}} parameter placeholder for the target Entity, Record field, or IOC.
Examples:
Run a google search on the action target
https://www.google.com?q={{value}}
Check for the action target on AbuseIPDB
https://www.abuseipdb.com/check/{{value}}
The only required parameter in the URL is {{value}}. Depending on your use case, you can use other template parameters to insert timestamps in the action URL. For more information, see the following section.
Template parameters for Context Actions
The table below defines the parameters you can use in the URL template for a Context Action.
Value
(Required) The {{value}} parameter inserts the target of the context action, for instance an IP Address to be inserted into the URL to a threat intel service. For example:
https://www.abuseipdb.com/whois/{{value}}
Record value
You can insert any field from the target of a Context Action into the action URL with the {{field_name}} placeholder. For example, you could include device_ip in the URL with {{device_ip}}.
Sumo Logic Base URL
The {{sumobaseurl}} parameter applies to Context Actions that run a Sumo Logic log search.
Assuming your CSE instance is configured to communicate with the Sumo Logic platform, when you create an action that runs a Sumo Logic search, CSE will automatically insert this placeholder in your URL template—you don’t need to explicitly insert {{sumobaseurl}} placeholder yourself.
Timestamp
When you run an action on a CSE Record, if that Record has a timestamp field value, you can insert the timestamp in UTC format into the URL using the {{timestamp}} parameter.
Formatted timestamp
To insert a Record’s timestamp field value into the action URL as a Unix timestamp, use {{timestamp [ms]}}.
Timestamp with delta
If desired, you can insert a timestamp value that is some offset of the Record’s timestamp field in the action URL, for example:
{{timestamp-5h}}
Supported operators
- + (Positive Delta)
- - (Negative Delta)
Supported units (case-sensitive)
- Y (year)
- M (month)
- W (week)
- D (day)
- h (hour)
- m (minute)
- s (second)