About the Software Development Optimization Solution
Organizations are automating their software application development lifecycle with a process known as Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD). The core foundation of CI/CD is automating software development, test, and build processes to increase development velocity and quality without creating extra work for the developers and operations teams.
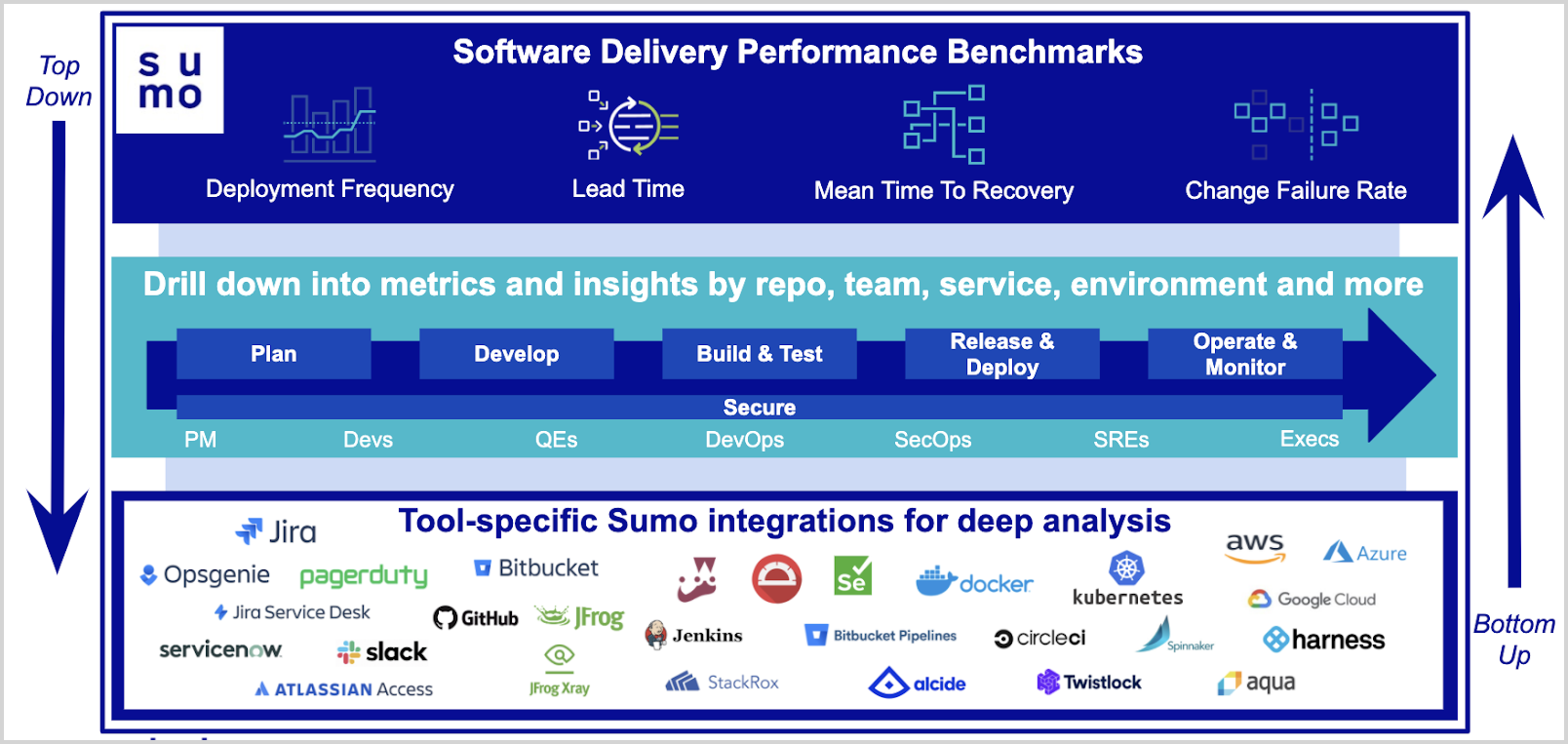
Sumo Logic enables CI/CD by giving development, QE, DevOps, SecOps teams a single pane of glass to measure and monitor KPIs or metrics developed by the DevOps Research and Assessment (DORA) organization for measuring the effectiveness of the software development and delivery process and the ability to monitor and troubleshoot their pipelines and incident management processes by analyzing real-time data from various stages in CI/CD pipelines and DevOps tools.
Overview of the Software Development Optimization Solution
The Software Development Optimization Solution enables you to effectively manage and enhance your development and production environments by providing you the following capabilities:
- Centralized data across the pipeline helps teams adopt a data-driven approach for collaboration and improvement.
- Navigation from executive dashboards to phases in the pipeline to individual tools to seamlessly measure software development productivity and quickly troubleshoot and unblock issues in the pipeline that helps in accelerating the software development cycle.
- Unified visibility across the CI/CD pipeline with streamlined setup and pre-built dashboards for the most popular DevOps tools.
The DevOps Lifecycle
The Software Development Optimization solution references the following phases in the DevOps Lifecycle, which are commonly used by most organizations:
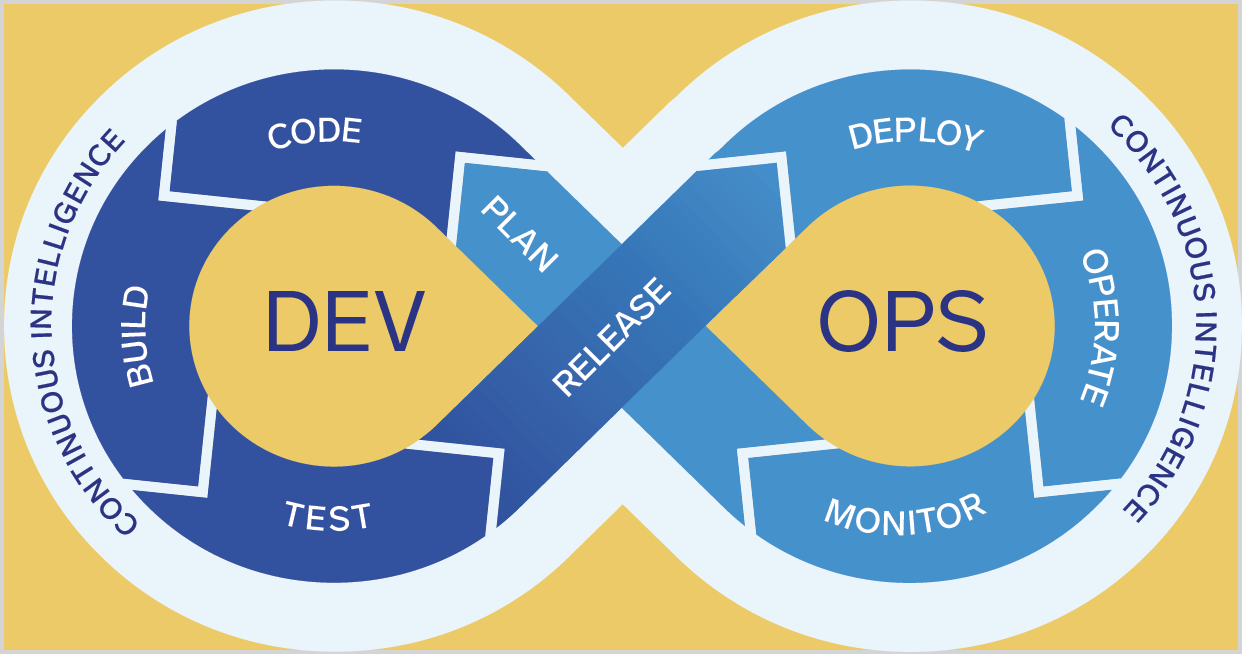
Plan. In this phase, requirements for specific work items, tasks, bugs, issues are documented and assigned to the right teams or individuals. In addition, feedback is gathered from stakeholders, customers, and product road maps to guide future development.
Tools most commonly used in this phase are Jira, GitHub, GitLab, Asana, and Azure DevOps.
Code. In this phase, an individual developer picks up a body of work in the Plan phase and implements it in the form of code and/or configuration artifacts. The developer uses a source code repository to check-in, review, and change code. The source code repository manages the various versions of code that are checked in, so developers do not write over each other’s work.
Tools most commonly used in this phase are Git, GitLab, Subversion, Cloudforce, Bitbucket, and TFS.
Build and Test. In this phase of the pipeline, code from in the source code repository is compiled into executable artifacts, after which a series of automated unit and regressions tests are run to ensure the executable code is ready to be deployed. If the build fails, or any of the tests fail, the developer is notified to resolve the issue. By continuously checking code changes into a shared repository and running builds and tests, organizations can minimize integration issues that arise when working on a shared codebase, and highlight breaking bugs early in the development lifecycle.
Tools used in this phase are Jenkins, GitLab, SonarQube, CircleCI, Artifactory, Selenium, and Water.
Deploy and Release. In this phase, a build is certified as ready for deployment and will be deployed to different environments for additional testing. A build is certified as a release candidate after it passes all tests and is then deployed in a production environment. By this stage, each code change has passed a series of manual and automated tests, and the team is confident that breaking issues and regressions are unlikely.
Tools most commonly used in this phase are Jenkins, Harness, GitLab, CircleCI, and Spinnaker.
Monitor and Operate. The operational phase in DevOps is where the production apps are actively managed by the DevOps and SRE team. All issues whether customer-facing or not typically flow through an incident management process and troubleshooting of apps is performed across the application and infrastructure stack. It is in this phase where auto-scaling of the infrastructure running the apps takes place.
Tools most commonly used in this phase are Cloud platform stacks, Jira, Opsgenie, and PagerDuty.