Preconfigure a Machine to Collect Remote Windows Performance Monitoring Logs
Use the instructions in this topic to preconfigure a machine to work with the Remote Windows Performance Monitor Log source.
Domain user and Collector setup
In order to setup the Collector to pull windows perfmon logs, there are some prerequisite tasks you must perform:
- The Collector must belong to the same domain as the systems it's going to collect from.
- You must create a domain user, who also belongs to local administrator group on the target machine.
- Windows firewall must be configured to allow RPC connections inbound.
- Remote Registry service must be running.
- NetBIOS over TCP/IP must be enabled.
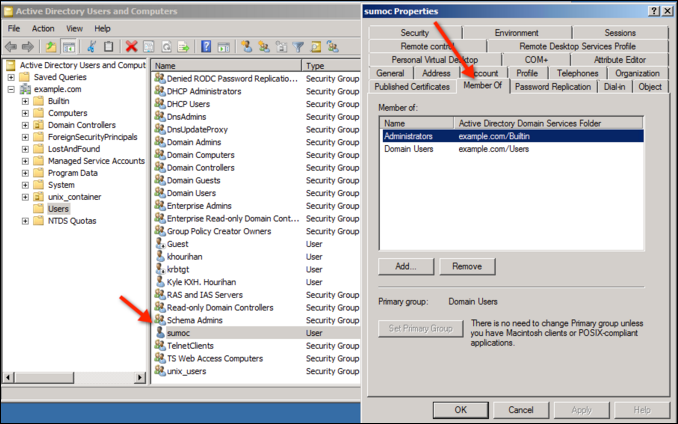
Set up domain and local administrator user
Create a domain user, who belongs to the local administrator group on the target machine.
Set up Windows Firewall on the Target Machine
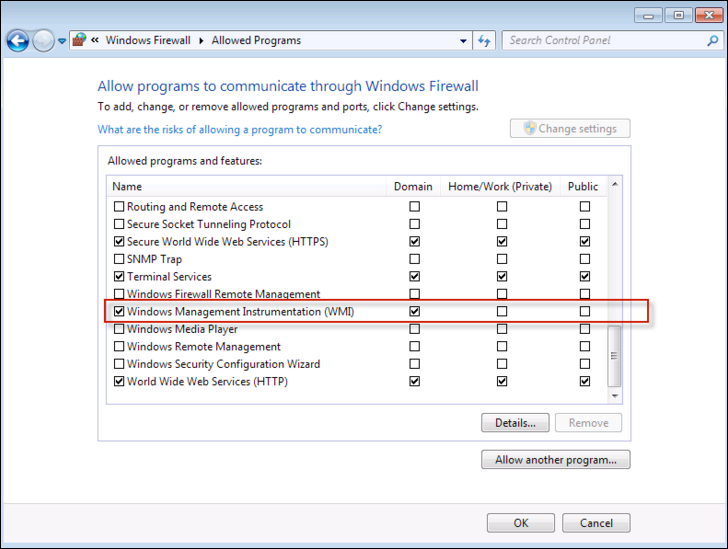
Open up the Windows firewall from the Control Panel.
On the left panel, click Allow a program or feature through Windows Firewall, check Windows Management Instrumentation, and save your change.
Configure to allow RPC traffic
Go to Firewall > Advanced settings > Inbound Rules > New Rule, on the popup window.
Choose Custom.
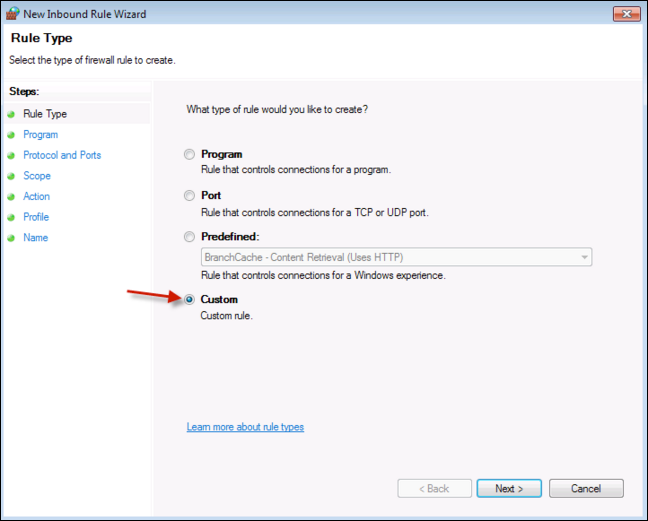
Click Next, then choose All Programs.
Then select Protocol and Ports:
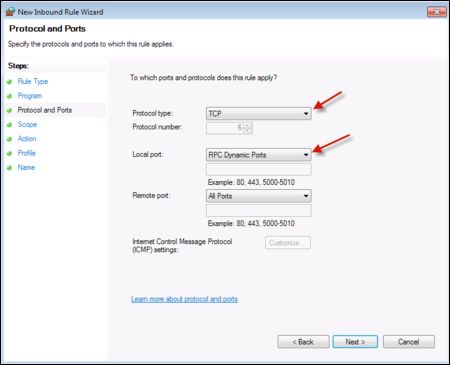
Select the Windows Protocol and ports. Use:
- Protocol Type: TCP
- Local Port: RPC Dynamic Ports
Ports required for communication are:
- TCP Port 135 (DCE/RPC Locator service)
- TCP Port 139 (NetBIOS Session Service)
- TCP Port 445 (Windows shares)
- UDP 137
- UDP 138
Click Next, then enter the IP restrictions (optional, but more secure). The local address should be the network address the Collector will connect to. The remote address should be the IP address the collect will use to talk to this Windows system. In the following screenshot, it's set to Any IP address.
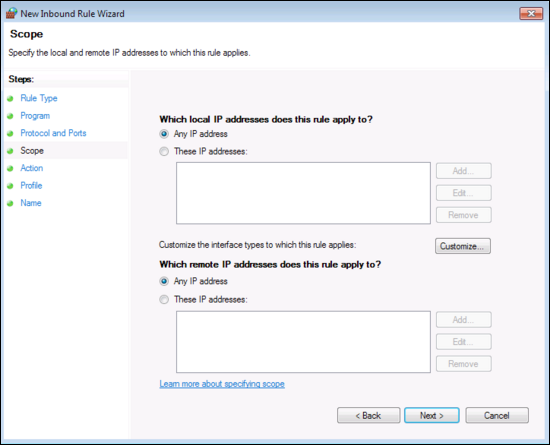
Click Next, then Select Allow the connection.
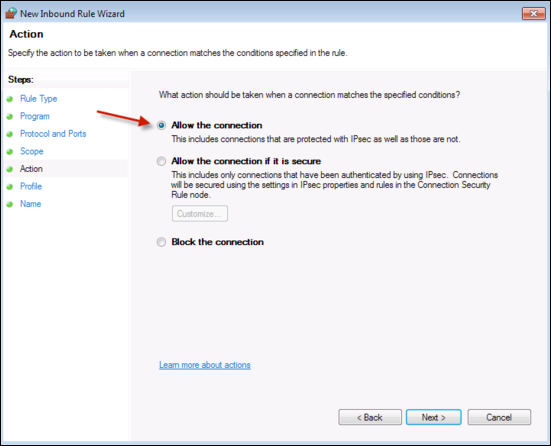
Click Next, then select the Domain.
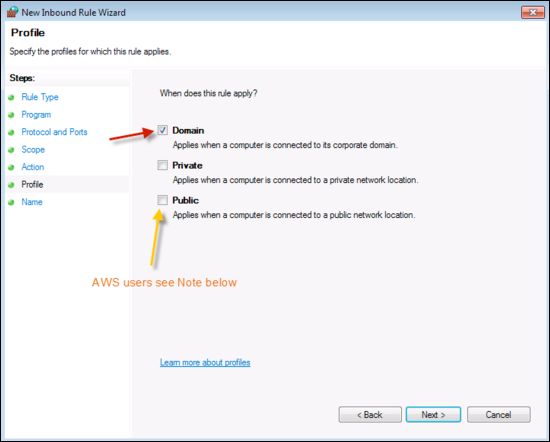
note
For Amazon users, Windows AMIs not in a domain should tick "Public". AWS AMIs consider their LAN interfaces to be on a public network by default.
1. Give the rule a name, for example, "Allow Sumo Logic Collector IN".
Grant Admin full control to Registry Key
Launch regedit.exe as Administrator.
Find the following registry key:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID{76A64158-CB41-11D1-8B02-00600806D9B6}Right-click and select Permissions.
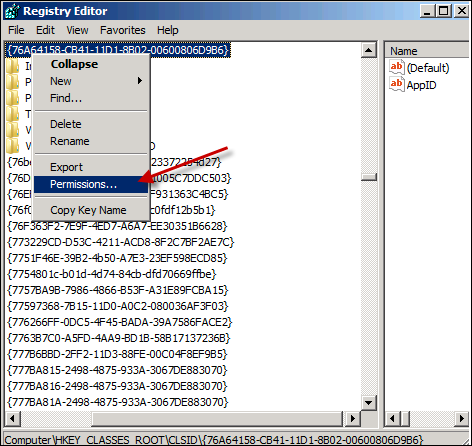
Click Advanced.
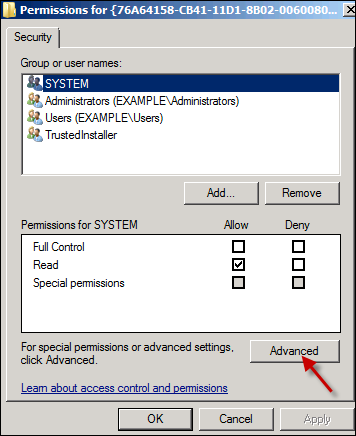
Click the Owner tab, and set the new owner as Administrators (group).
Click Apply. By default, windows sets the owner to Trustednstaller, which doesn't work. We switch it to be owned by the Administrators group, which your user is a "MemberOf".
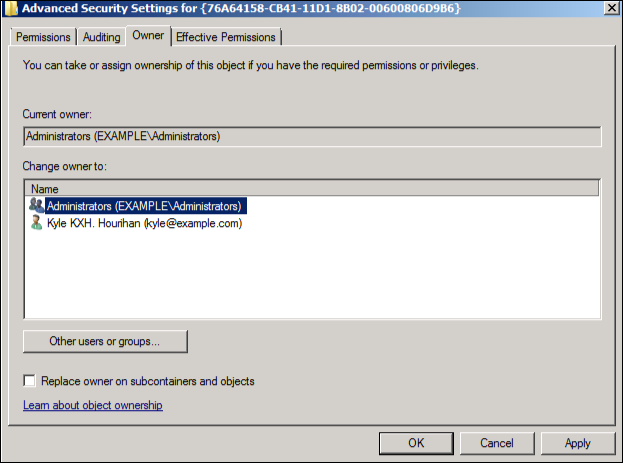
Click OK. You will be returned to the main permissions page and set the new owner, Administrators, to have full control of this object:
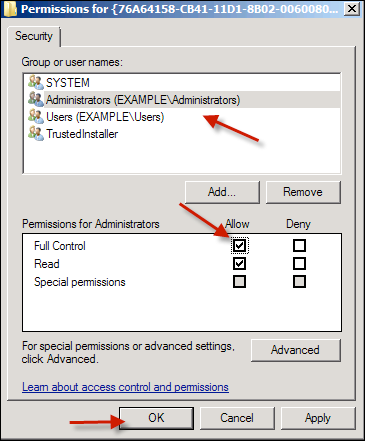
Click OK.
Repeat steps 3-9 for the following registry key (if it exists):
HKLM\Software\Classes\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{76A64158-CB41-11D1-8B02-00600806D9B6}Finally, from services.msc, restart Remote Registry Service.
These registry key changes are necessary because Sumo Logic leverages Jinterop, a Java-DCOM bridge, to communicate with the remote machine and gather perf logs via WMI through DCOM. Several major software vendors have documented a requirement to make a similar change in order to allow script access.
The reason that the key's owner is changed from Trustedinstaller to Administrators is so that Sumo Logic can grant Administrators full control. If you can directly grant Administrators full control via GPO, you can skip this step. You can also change the owner back to Trustedinstaller afterwards.
Troubleshooting
The Collector comes with a PowerShell script that can be used to verify or apply the above configuration automatically on a list of remote systems. The script is located in the Collector installation directory, at .\powershell\perfmon\sumo-remote-collector-config.ps1. A detailed usage page can be seen by running the command Get-Help .\sumo-remote-collector-config.ps1 -Full from the script's directory.
The following command checks for connectivity based on user permissions,firewalls, or registry keys:
C:\Program Files\Sumo Logic Collector\powershell\perfmon\sumo-remote-collector-config.ps1 -computernames "<name>" -credential $ps_cred -check
The following command may address a registry permissions issue if present:
C:\Program Files\Sumo Logic Collector\powershell\perfmon\sumo-remote-collector-config.ps1 -computernames "<name>" -credential $ps_cred -apply
Enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP
- Click Start, and then click Network. (Click Start, type **ncpa.cpl** into the search box for Windows 7 or Vista, and hit ENTER.)
- Click the Network and Sharing Center.
- Click Manage Network Connections.
- Right-click the Local Area Connection and select Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
- Click the Advanced button under the General tab.
- Click the WINS tab.
- Click Enable NetBIOS Over TCP/IP.
- Click OK and exit the settings.
Validating Dynamic RPC Port Access Through Firewalls
On Windows Vista and 2008+, the default dynamic port range is 49152-65535. On older Windows systems, the default dynamic port range is 1025-5000.
Make sure that:
- The firewall is properly configured on the remote machine. Dynamic port ranges must be open.
- If the remote machine IP is mapped to the range (10.*.*.*, 172.16>31.*.*, 192.168.*.*) and the Collector machine is not in the same private network then the remote machine will not be accessible.
- Run port query to check if the remote machine ip:port is listening.
Download https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17148
portqry -n ip -p tcp -o port
portqry -n ip -p tcp -o 135,139,445
portqry -n ip -p udp -o 137,138
If the response is "FILTERED", then a firewall or VLAN could be blocking the port.
If the response is "NOT LISTENING", then Sumo Logic can get to the machine, but it is not listening on that port number.
If you use a more strict Firewall policy and need to reduce the range of ports that are open, refer to the following Microsoft Technet article on how to restrict RPC port ranges in Windows: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/15459