How can I tell if I'm collecting data?
After installing a Collector and configuring a Source, your data should appear in Sumo Logic in a matter of minutes. How can you confirm that your data is being collected? Try any of the following options.
Check the Status page of the Sumo Logic Web Application
In Sumo Logic select Manage Data > Collection > Status to view the total message volume (the volume of all Collectors in your account) and the volume of data from each Collector.
As long as you see that some messages are present, your Sumo Logic account is up and running.
note
Make sure that you're viewing Running Collectors or All Collectors in the Status page. If the Stopped Collectors option is selected, you won't see accurate message volume information.
Try a search
Collected data should be searchable within a couple of minutes. You can run a search based on when Sumo Logic received your data by running a search by Receipt Time. Try specifying the Collector with the metadata field _collector and the Collector name, like _collector=<name>.
If your user account is not an administrator check your Role assignment for any search filters that may be restricting access to the data.
Verify that your Collectors are running
Collectors and Sources in your account are listed on the Collectors page. Collectors and Sources that are running (able to communicate with Sumo Logic and configured to send data) are marked with . Stopped Collectors and Sources are marked with
. Stopped Collectors don't send any data.
If a Collector is stopped, you can verify the Collector's status and restart it if necessary.
To check a Collector's status:
On the host with the Collector navigate to the Collector's [install_dir]/ and run
#./collector status. The default Collector installation locations are:- Linux:
/opt/SumoCollector/or/usr/local/SumoCollector - Windows:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Sumo Logic CollectororC:\Program Files\Sumo Logic Collector
- Linux:
If the status is "stopped" you can restart the Collector by running
#./collector start.Running a Collector on Windows? The Collector's status can be found by running services.msc from an Admin cmd.exe shell, or from the Control Panel. The service is listed under SumoLogic Collector; the startup type should be set to Automatic.
Check timestamp settings
If your log files have missing or faulty time stamp data it can affect the log messages you'll see collected; search results are also affected if time stamp information is incorrect. For example, if a Collector is running on a computer that doesn't contain a UTC offset time (like UTC-0800), the time stamp could be off by several hours, so if you attempted to search logs within the past 15 minutes no search results will appear.
When you configure a Source, you can choose one of three timestamp options. First, make sure that your log data is using a supported timestamp and date format.
To view Source settings:
select Manage Data > Collection > Collection.
Click Edit to the right of the Source's name.
Under Advanced, choose one of the following:
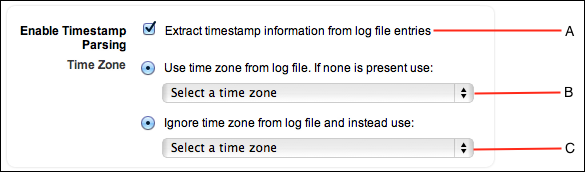
- Extract timestamp information from log file entries. Select this option if you'd like Sumo Logic to always extract timestamps from log messages. If no timestamp is detected, Sumo Logic uses the time when the data is received. Generally, this is the best option (it's also selected by default).
- Use time zone from log file. Choose a time zone that Sumo Logic can use if log files don't have a time stamp. If a Collector is running on a computer set to the UTC time zone without an offset, Sumo Logic will use this time zone.
- Ignore time zone from log file. Choose a time zone to override any time zone information found in log files. If you're collecting log files from disparate time zones, choose this option to set all your Sources to the same time zone.
important
Changes you make to this option aren't applied retroactively; they are applied to log messages moving forward.
For more information, see Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats.