CSE APIs
This page has information about accessing the CSE APIs and API documentation. The process depends on your CSE environment.
- If your CSE URL ends in
sumologic.com, follow the instructions in Access APIs from Sumo Logic Platform. - If your CSE URL ends in
jask.ai, follow the instructions in Access APIs from CSE.
Access APIs from Sumo Logic Platform
If your CSE URL ends in sumologic.com, follow the instructions in this section. If your CSE URL ends in jask.ui, follow the instructions in Access APIs from CSE.
Your API endpoint depends on your Sumo Logic deployment. For a list of Sumo Logic API endpoints by deployment, see Sumo Logic Endpoints and Firewall Security. Your endpoint will look something like this:
https://api.us2.sumologic.com/api/
To view API documentation, go to the /docs/sec path at your API endpoint. For example:
https://api.us2.sumologic.com/docs/sec/
The APIs themselves start with /api/sec/v1/
For example:
https://api.us2.sumologic.com/api/sec/v1/custom-insights
API requests must be authenticated. For authentication options and information about rate limiting, see API Authentication.
Access APIs from CSE
If your CSE URL ends in jask.ai, you can access the API docs by clicking the question mark (?) icon in the upper right corner of the CSE UI, and selecting API Documentation.
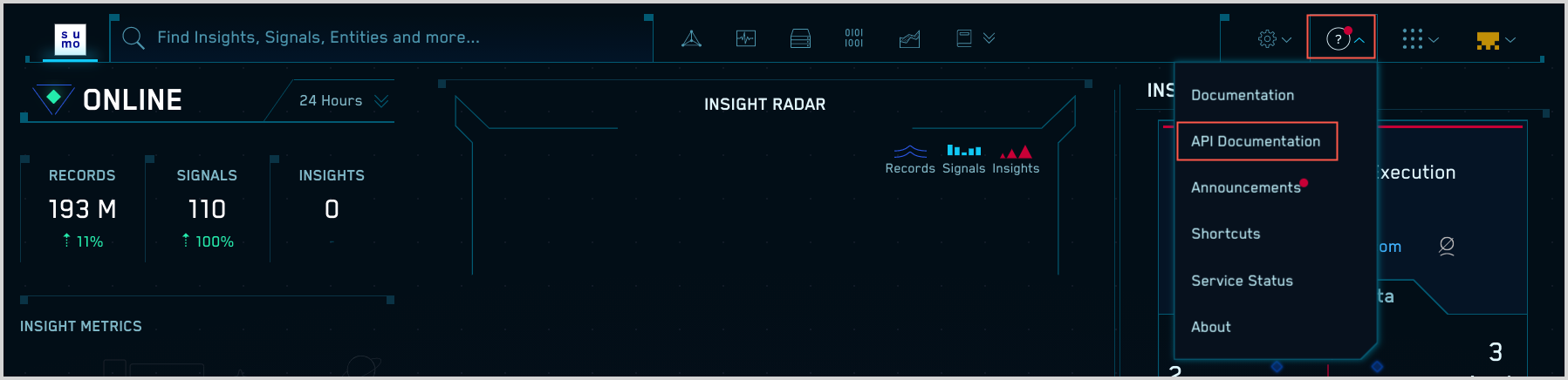
You can also access the API docs by pointing your browser directly to:
<my-cse-url>/api/v1/docs
Where <my-cse-url> is the URL you use to access the CSE UI.
Authentication
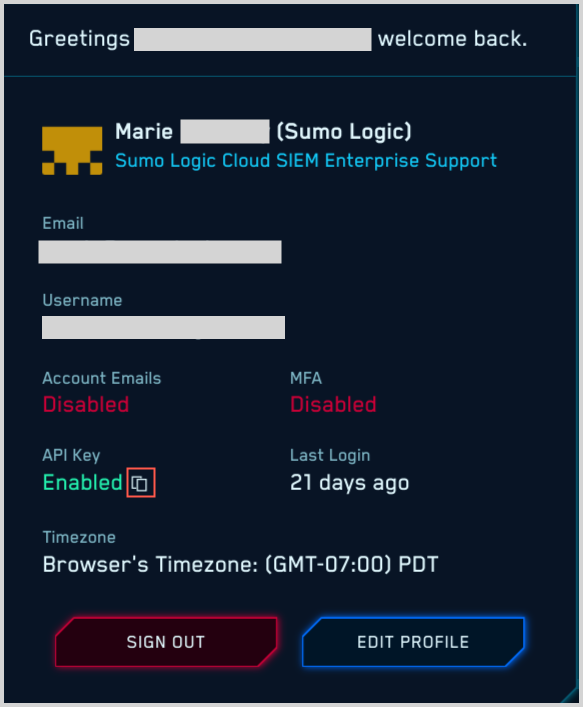
The APIs require authentication using an API key specified in the X-API-Key. You can find your API key by clicking the profile icon in the upper right corner of the CSE UI.
![]()
In your profile, click the copy icon for the API key to copy your API key.
Rate Limiting
The Sumo Logic CSE API is rate limited. The rate limit is 1,000 requests per minute. That limit is subject to change without notice.
Each API response contains the following headers:
X-RateLimit-Limit—Contains the total number of requests allowed for the current time period.X-RateLimit-Remaining—Contains the number of requests remaining in the current time period.X-RateLimit-Reset—Contains a timestamp (UTC seconds since epoch) for when the current time period ends and the limit will be reset.
If you exceed the rate limit, you’ll receive an HTTP 429 Too Many Requests error in response. This response will also contain a Retry-After header, which contains the number of seconds until the current period ends and the rate limit is reset.