Collect metrics from VMware vRealize Operations Manager 8 Enterprise
With vRealize Operations Manager (vRops) software, you can proactively identify and solve emerging issues with predictive analysis and smart alerts, ensuring optimal performance and availability of system resources - across physical, virtual, and cloud infrastructures.
This page provides instructions for collecting metrics from vRops. Click a link to jump to a topic:
- Step 1: Set up a server, host, or VM to collect data
- Step 2: Download and install the Collector
- Step 3: Collect metrics from vRops
- Step 4: Encrypt passwords
- Troubleshooting
Step 1: Set up a server, host, or VM to collect data
This section provides instructions for installing the Sumo Logic scripts for metrics on a vCenter server, or another host with access to vRops APIs.
Installing Sumo Logic scripts on a vCenter server, another host, or VM
This section walks you through the process of installing Sumo Logic scripts for metrics on a vCenter server, or another host with access to vRops APIs. Finally, it provides instructions for configuring the path to run the scripts, whether on a vCenter server, host, or VM.
To install and configure the Sumo Logic scripts, do the following:
important
Without adequate permissions (read/write/execute) for the directories in which the scripts reside, unexpected script errors will occur.
Without adequate permissions (read/write/execute) for the directories in which the scripts reside, unexpected script errors will occur.
On the Server, host, or VM create a directory in which to house the Sumo Logic scripts for vRops collection. We recommend that you name the directory /var/log/vmware, or something similar.
Clone the Sumo Logic VMware vRops repository into the directory you just created.
Install python version 3.6 or later.
Download and install the Nagini module from vRealize Operations Manager. It can be found at
"https://<vrops-server>/suite-api". Visit the page and download the Python client (Nagini) at the bottom of the page. Install the Nagini module by following the readme included in the package. Nagini requires the python requests package. The Sumo Logic solution has been tested on the Nagini version 2.0 and requests version 2.6 and 2.24.Verify that the user account that will be running the Sumo Logic vRops scripts has full read/write/execute permissions for the directories in which the collection scripts will be extracted. sumo-vsphere-ulm.zip
important
Without adequate permissions (read/write/execute) for the directories in which the scripts reside, unexpected script errors will occur.
Edit the cron_vrops_metrics.sh script, changing the
SCRIPT_PATHvariable to reflect the absolute path where the script resides.
note
If you have multiple vRops servers, create a new line for each one.
Step 2: Download and install the Collector
An Installed Collector is a Java agent that receives logs and metrics from its Sources and then encrypts, compresses, and sends the data to the Sumo service. The Collector runs as a service and starts automatically after installing or rebooting.
To install a Collector to collect logs and metrics, see Installed Collectors for installation instructions.
Step 3: Collect metrics from vRops
This section explains how to set up a vCenter server, host, or VM to collect logs and metrics vRops.
Collecting metrics
Collecting performance metrics involves using scripts to call the vRops API to extract performance statistics.
Metric data collection for vRops servers works by getting data from vRops server in parallel, using multiple threads. The number of threads depends on the amount of data you are collecting and the frequency of the collection.
The number of threads can be controlled using a property THREADSIZE_POOL in the config.json config file. You can also control the number of objects processed by a single thread using the property BATCH_SIZE. The following is a description of all the configuration properties.
BATCH_SIZE: Default 50, Simultaneous objects processed by a single thread for retrieving the metrics.DEFAULT_THREADSIZE_POOL: Default 4, Number of threadsSSL_VERIFY: Default False, if using SSL, set as TrueSSL_CAPATH: Certificate absolute path ifSSL_VERIFYis TrueBACKFILL_HOURS: Default 1, number of backfill hours for which to get metrics for.GET_ALL_METRICS: Default False, Get all metrics for all resources. Not recommended on Production servers as the number of resources and metrics will be huge.resources: Used for getting specific metrics for specific resources. This is an array of resource objects that specify which metrics to retrieve for which resources. You can add/remove a separate section for each resource along with the metrics to be retrieved.For Example:
"resources": [
{
"adapterKind": "VMware",
"keys": [
"guestfilesystem|capacity_total",
"cpu|capacity_provisioned",
"cpu|numberToRemove",
"cpu|numberToAdd",
"cpu|demandmhz",
"guestfilesystem|usage_total"
],
"resourceKind": "VirtualMachine",
"sampleno": 1
}
]adapterKind: VMware vRops adaptor kind.keys: Name of the metrics to be retrieved. Example list for Virtual Machines.resourceKind: The actual resource kind such as a VirtualMachine.sampleno: Number of samples to retrieve. Recommended value is 1.
To collect performance metrics, do the following:
Follow the instructions to configure a Streaming Metrics Source. Make sure that the Content-Type is set to Carbon1.
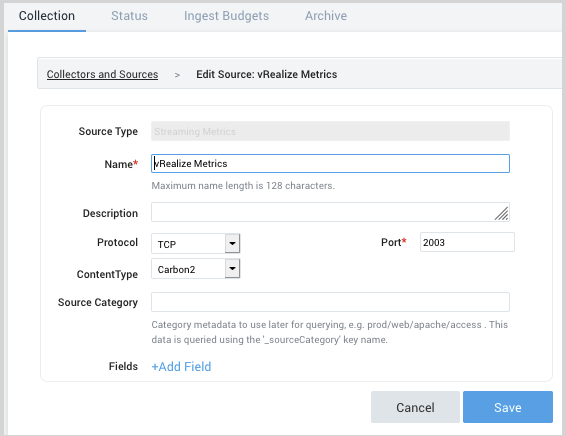
Edit the properties in the bundled config.json properties file, as necessary.
Go to the directory for the Sumo Logic scripts, and run the sumologic-vrops-metric-collection.py script—which queries the vRops Server for metrics—from that location with the following command:
python3 sumologic-vrops-metric-collection.py -u [vrops_username] -p [vrops_password] -s [vrops server] -t [target server] -to [target port]Example 1: Using metrics streaming source and specific log directory with a specific log file prefix.
# python3 $SCRIPT_PATH/sumologic-vrops-metric-collection.py -s 192.168.124.29 -t sumologic_host -to sumologic_host_port -u vropsadmin -p vropsadmin -l /var/log/vmware/log/metricsExample 2: Using specific log directory with a specific log file prefix and encrypted Password.
# python3 $SCRIPT_PATH/sumologic-vrops-metric-collection.py -s 192.168.124.29 -t sumologic_host -to sumologic_host_port -u vropsadmin -cf $SCRIPT_PATH/custom_config.json -l /var/log/vmware/log/vrops_metrics -pK 'xgb8NJ3ZYPJbzX6vWHySZbLd73bKWPsGMKoSnry7hL4=' -p 'gAAAAABb6asvlRfxEj_ZQTKOyrqnGNMbfo_kpxrqv4DCO6TorS4FmKFzrepe0_xtiMT67ZT6OOf5bfrVZXNnUDFNlwPWrpFSfg==' -pE TrueThe script supports the following parameters:
-s: Remote vRops Server to connect to. Required Parameter.-o: Remote vRops Server port to use, default 443. Optional.-u: User name to use when connecting to vRops server. Required.-p: Password to use when connecting to vRops server. Required.-ts: Timestamp File. Default ‘.timelog_metrics’.-t: Target Sumologic syslog server. Required.-to: Target Sumologic port to use, default 2003. Optional.-cf: Configuration File, default config.json. Optional.-l: Log File Prefix. Default:vrops_metrics_. By Default the log file is created in the execution directory. Full log path and log prefix can also be specified for example:-l C:\Users\user6\vrops_metrics, wherevrops_metricsis the log prefix and is required. The log file is created with prefix + current timestamp.-pE: Is the password encrypted? Default False. Optional.-pK: Encryption Key for Password. Required if-pEis True.
In Sumo Logic, verify that metrics are being captured.
When you are satisfied with the batch and thread configurations, modify the cron_vrops_metrics.sh with the required parameters and create a cron job to periodically run the cron_vrops_metrics.sh script at the desired time interval.
- The cron job needs to be run as root, or as a user who has read and write access to the script directories.
- For more detailed information, see the shell script for configuration options
Sample CRON job to periodically run the cron_vrops_metrics.sh script every 15 minutes, use the sudo crontab -e option and add the following line:
*/15 * * * * /var/log/vmware/cron_vrops_metrics.sh
Step 4: Encrypt passwords
The scripts support symmetric authenticated cryptography—also known as secret key authentication—using the python Fernet implementation.
To utilize encryption**, generate a key from the python command line:
>>> from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
>>> print(Fernet.generate_key())
b'xgb8NJ3ZYPJbzX6vWHySZbLd73bKWPsGMKoSnry7hL4='
Encrypt the password, from the python command line:
>>> from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
>>> key = b'xgb8NJ3ZYPJbzX6vWHySZbLd73bKWPsGMKoSnry7hL4='
>>> s = Fernet(key)
>>> text = s.encrypt(b"secretpassword")
>>> print(text)
b'gAAAAABb6asvlRfxEj_ZQTKOyrqnGNMbfo_kpxrqv4DCO6TorS4FmKFzrepe0_xtiMT67ZT6OOf5bfrVZXNnUDFNlwPWrpFSfg=='
Modify the scripts to include the encrypted password and the key.
For Example:
python3 sumologic-vrops-metric-collection.py -u [username] -pK 'xgb8NJ3ZYPJbzX6vWHySZbLd73bKWPsGMKoSnry7hL4=' -p 'gAAAAABb6asvlRfxEj_ZQTKOyrqnGNMbfo_kpxrqv4DCO6TorS4FmKFzrepe0_xtiMT67ZT6OOf5bfrVZXNnUDFNlwPWrpFSfg==' -s 192.168.20.121 -t 127.0.0.1 -to 2003 -pE True
note
The pE flag is used to specify whether the password is encrypted or not. Default is false.
Troubleshooting
- The scripts need to read and write access to the directory to generate logs and maintain timestamps.
- Python must be installed, as the scripts use python.
- Scripts generate logs that can be reviewed if problems arise.
- The logs are generated for each run under the configured working directory.
- If the collector is not running but the script is, the metrics will be lost. In such a case, once the collector is running again, update the epoch timestamp (in milliseconds) in the .timelog_metrics to the required start time. This will allow you to retrieve the old data. After the script retrieves the old data, it continues with normal processing.