backshift
The backshift operator helps you compare values as they change over time. It simply shifts the data points it is given and returns them in your results in a new field.
The backshift operator can be used with rollingstd, smooth, or any other operators whose results could be affected by spikes of data (where a spike could possibly throw off future results).
It is important to note that backshift does not automatically add timeslices, nor does it do any sorting. You can manually add other operators in the query to add timeslices, for example, and any kind of sorting you'd like to include. To add time-series analysis, add _timeslice | ... | sort + _timeslice before the backshift operator in the query.
Syntax
backshift <field> [, shift_length] [by <field>]
Rules
- An alias for
backshiftis optional. When an alias is not provided,_backshift** **is the default alias. - Specified fields must contain numeric values.
- To add a query that includes a
backshiftoperator to a dashboard, you must add a group by function before thebackshiftoperator. - The default window length (
shift_length) is 1. - The maximum window length is 1000.
Example
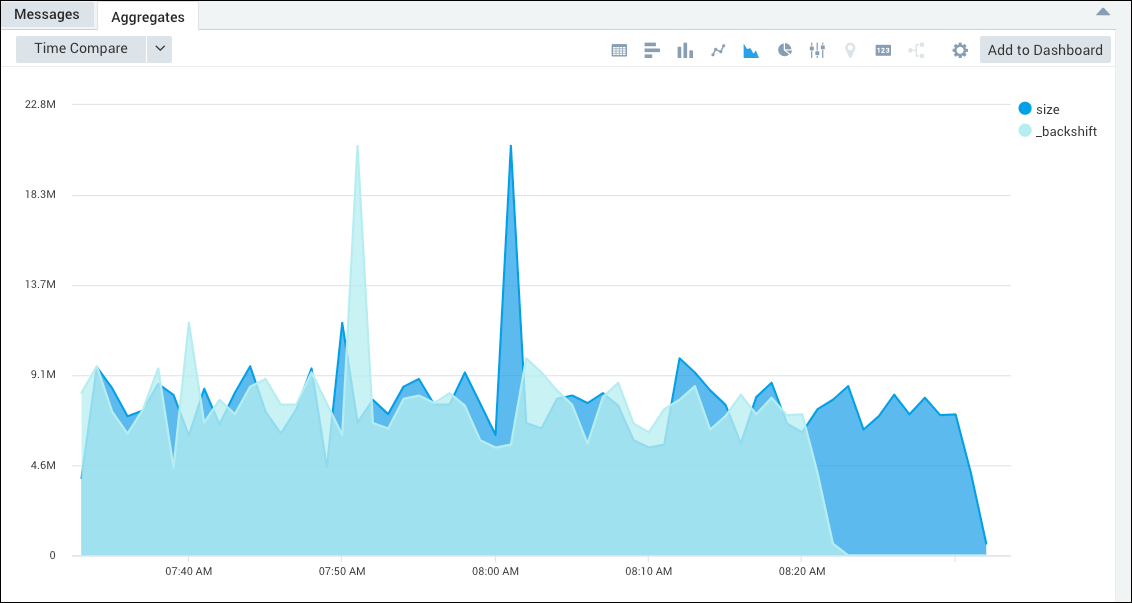
Use backshift to see the difference of fields between time points.
Running a query like this:
_sourcecategory=Labs/Apache/Access
| timeslice by 1m
| count by _timeslice
| sort + _timeslice
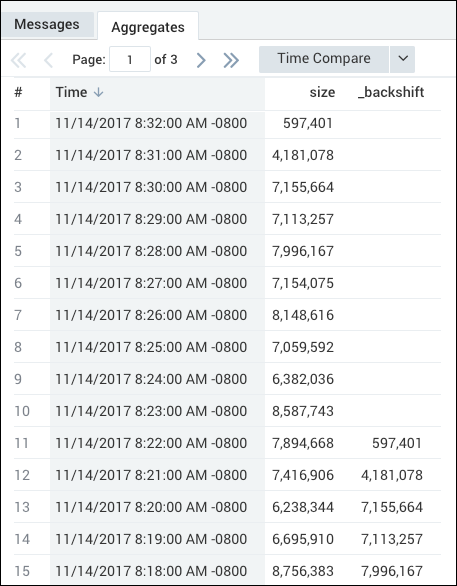
| backshift _count,10 as size
produces results like:
Then you can visualize the results as an area chart.