smooth
The smooth operator calculates the rolling (or moving) average of a field, measuring the average of a value to "smooth" random variation. Smooth operator reveals trends in the data set you include in a query.
Within a query that contains a smooth operator you will choose a window (described as window_length in the syntax below); the average of the values within the window creates a data point.
If you specify a window length of 5, but only 4 data points are available, the smooth operator takes the average of whatever is available.
Adding a group by function to a smooth operator query produces a running average within each group (with data from each group calculated separately).
Syntax
smooth <field> [, <window length>] [as <field>]
Rules
- An alias for smooth is optional. When an alias is not provided, _smooth is the default alias.
- The specified field must contain numeric values.
- To add a query that includes a smooth operator to a Dashboard, you must add a group by function before the smooth operator.
- The default window length is 10.
- The maximum window length is 1000.
Examples
The following examples use the sort operator to sort the time prior to calculating the rolling average with smooth.
Use smooth to see the difference of fields between time points, grouped by source host
Running a query such as:
_sourcecategory=katta
| timeslice by 1m
| count by _timeslice,_sourcehost
| sort + _timeslice
| smooth _count, 50 by _sourcehost
produces results like:
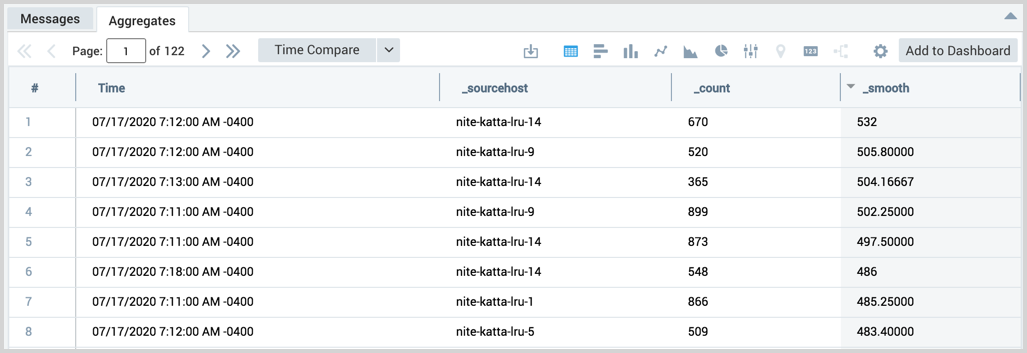
Smooth the difference of a quantity between time points
Using smooth with timeslice, you can run a query similar to:
* | parse "bytes transmitted: '*'" as bytes
| timeslice 1m
| sum(bytes) as bytes by _timeslice
| sort _timeslice
| smooth bytes, 5
that produces results like:
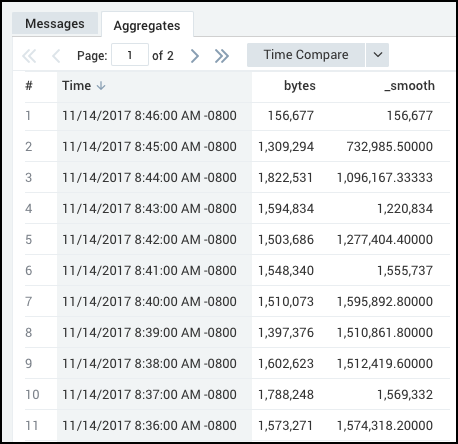
Use backshift with smooth and rollingstd to view the averages of incoming bytes
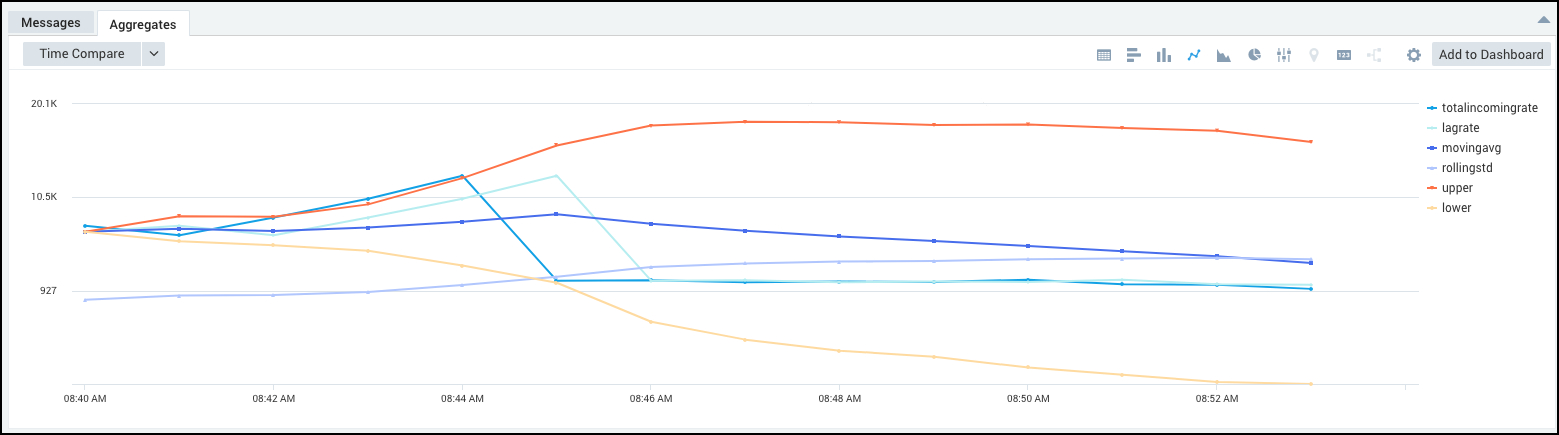
Running a query like:
...| timeslice by 1m
| avg(oneMinuteRate) as avgRateByHost by _sourcehost,_timeslice
| sum(avgratebyhost) as totalIncomingRate by _timeslice
| sort + _timeslice
| backshift totalIncomingRate, 1 as lagRate
| smooth lagRate,10 as movingAvg
| rollingstd lagRate,10 as rollingStd
| movingAvg + (3 * rollingStd) as upper
| movingAvg - (3 * rollingStd) as lower
produces results similar to:
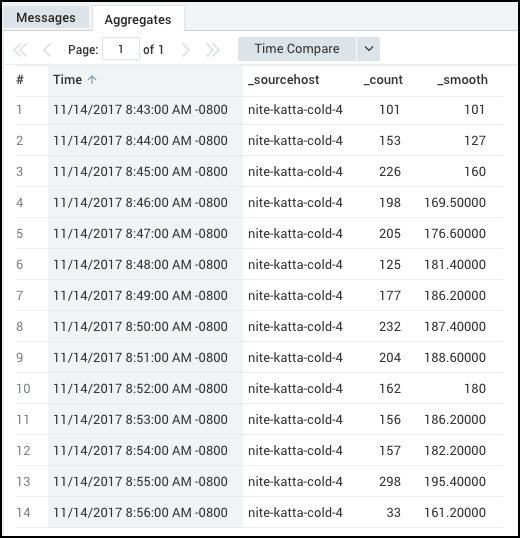
Specify a window length of 5, but only 4 data points are available
Before 5 values are available, the smooth operator takes an average of whatever is available. For example:
_sourcecategory=katta
| timeslice by 1m
| count by _timeslice,_sourcehost
| where _sourcehost="nite-katta-cold-4"
| sort + _timeslice
| smooth _count,5
produces results like: